이번에는 엄청 유명한 pix2pix 논문을 리뷰해보겠다. GAN 중에서 paired image set을 이용할 때 가장 많이 쓰고 보편적인 베이스라인이다. 랜덤 vector z 대신 input image를 condition으로 활용하면서 paired image를 이용해 학습하는 형태로 바뀌었다.
Introduction
- 목표
- Specific한 task들을 Image-to-Image translation이라는 하나의 common framework를 만든다.
- Traditionally, each of these tasks has been tackled with separate, special-purpose machinery, despite the fact that the setting is always the same : predict pixels from pixels.
-
GAN의 사용 이유
Coming up with loss functions that force the CNN to do what we really want e.g, output sharp, realistic images is an open problem and generally requires expert knowledge.
⇒ GAN : blurry images will not be tolerated since they look obviously fake.
-
cGAN의 도입
cGANs learn a conditional generative model. THis makes cGANs suitable for image-to-image translation tasks, where we condition on an input image and generate a corresponding output image.
Conditional GANs
-
Image-to-Image translation 중에서도 Per-pixel classification 또는 regression 문제는 output space를 ‘unstructured’로 본다.
(Each output pixel is considered conditionally independent from all others given the input image.)
-
반면 conditional GAN은 structured loss를 배운다.
(output의 joint configuration을 고려하여 loss를 penalize한다)
- 이것은 structured loss 함수들 (based on matching covariance statistics. ex. conditional random fields, SSIM metric, feature matching, nonparametric losses…)를 사용하는 것과는 다르지만, 어떤 구조던 간에 output과 target 간의 차이를 penalize 할 수 있다. (위의 1. common framework를 실행하는데 가장 알맞는 구조임을 설명한 것)
-
이전까지의 Image-to-Image translation 연구는 GAN을 unconditional하게 적용하는 연구밖에 없었다. 따라서 L2 regression과 같은 다른 term에 의지했다.
⇒ conditional GAN을 적용하면서 굉장한 결과 향상이 있다.
Materials and Methods
cGAN은 GAN과 달리 image x와 random noise vector z에서 y로의 매핑을 training한다. ( G : {x,z} →y ) 기존의 GAN이 가우시안에서 샘플링한 random noise vector z만으로 이미지를 생성했다면, cGAN은 image를 condition으로 받는다는 차이가 있다. 그러나 pix2pix에서의 cGAN은 image를 condition으로 받는 형태보다는 image자체를 input으로 받고 있는 형태가 강하고 paired image로 pixel loss를 이용하여 학습하기 때문에 기존의 GAN과 다르게 deterministic하게 작동한다.
Objective function
\[L_{cGAN}(G, D) =E_{x,y} [log D(x, y)]+E_{x,z} [log(1 − D(x, G(x, z))]\]unconditonal GAN의 objective (discriminator does not observe x) :
\[L_{GAN} (G, D) =E_y [log D(y)]+E_{x,z} [log(1 − D(G(x, z))].\]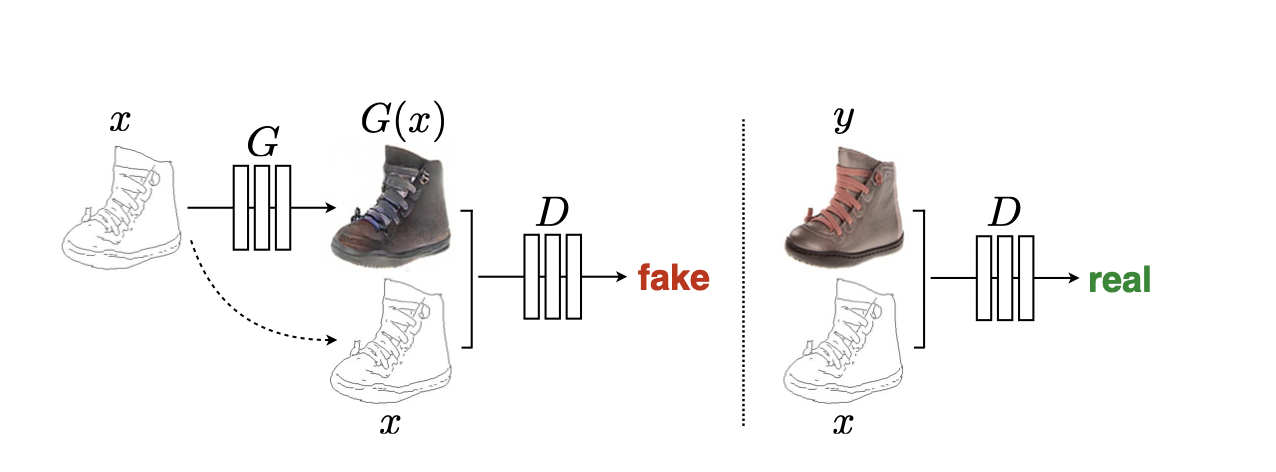
pix2pix처럼 이미지 자체를 input으로 받는 형태에서 generator의 x를 제거하기는 어렵기 때문에, discriminator 또한 이미지 자체를 condition으로 확인하는지 여부를 차이로 하여 cGAN과 GAN의 차이를 설명해놓았다.
cGAN objective를 단독으로 사용하는 대신 traditional loss와 mix(L2보다 덜 blurry한 L1 사용). 결국 paired set을 이용하도록 cGAN을 optimize했다고 볼 수 있다.
\[L_{L1}(G)=E_{x,y,z}[∥y−G(x,z)∥_1]\]최종 objective function: \(G∗ =arg\ \underset{G}{min}\ \underset{D}{max} \ L_{cGAN}(G,D)+λ_{LL1}(G)\)
Network architecture
- Generator와 discriminator 모두 convolution-BatchNorm-ReLu 사용
- Generator
- 단순한 encoder-decoder 구조 대신 UNet(skip connection이 있는) 구조를 사용
- Such a network requires that all information flow pass through all the layers, including the bottleneck.
- For many image traslation problems, there is a great deal of low-level information shared between the input and output, and it would be desirable to shuttle this information directly across the net.
- 단순한 encoder-decoder 구조 대신 UNet(skip connection이 있는) 구조를 사용
- Discriminator
- GAN과 함께 L1 loss 사용 : blurry한 이미지를 만드는 L2 대신 L1 loss를 사용
- this motivates restricting the GAN discriminator to only model high-frequency structure, relying on an L1 term to force low-frequency correctness
- low-frequency : coarse, high-frequency : refinement(디테일) 이라고 생각 됨.
- convolutional PatchGAN classifier (penalizes structure at the scale of image patches)
- only penalizes structure at the scale of patches (high-frequency를 모델링하기 위해서는 local image patch의 structure에 집중해야 한다)
- GAN과 함께 L1 loss 사용 : blurry한 이미지를 만드는 L2 대신 L1 loss를 사용
Experiment
- Graphic tasks (photo generation)
- Vision tasks (semantic segmentation)
- Semantic labels↔photo, trained on the Cityscapes dataset [12].
- Architectural labels→photo, trained on CMP Facades [45].
- Map↔aerial photo, trained on data scraped from Google Maps.
- BW→color photos, trained on [51]. • Edges→photo, trained on data from [65] and [60]; binary edges generated using the HED edge detector [58]plus postprocessing.
- Sketch→photo: tests edges→photo models on human-drawn sketches from [19].
- Day→night, trained on [33].
- Thermal→color photos, trained on data from [27].
- Photo with missing pixels→inpainted photo, trained on Paris StreetView from [14].
Evaluation metric
- Amazon Mechanical Turk (Human observer)
- real vs fake를 구분하는 task를 사람에게 맡김
- map generation, aerial photo generation, image colorization에 진행
- real img에 대해 pre-train된 classifier에게 그 안의 object들을 얼마나 정확하게 구별할 수 있는가를 metric의 척도로 이용
- FCN score
- cityscapes dataset에 진행
Result
Analysis of the objective function
L1 / cGAN 단독 / L1 + cGAN

- L1 단독으로 사용하는 경우 blurry한 이미지 생성
- 또한 colorfulness 관점에서, L1은 grayish한 색깔을 주로 생성 (it is uncertain which of several plausible color values a pexel should take on - L1 단독으로는 어떤 색을 써야 그럴듯한 색깔인지 판단할 수 없다)
- L1 will be minimized by choosing the median of the conditional probability density function over possible colors.
- cGAN 단독으로 사용하는 경우 훨씬 sharp한 이미지가 생성되나 visual artifacts가 나타남
- colorfulness : color가 unrealistic 하면 (grayish 하면) discriminator가 잡아내기 때문에 색깔이 L1 단독으로 쓸 때보단 다채로워짐.
- L1 + cGAN의 경우가 가장 결과가 좋음
cGAN / GAN
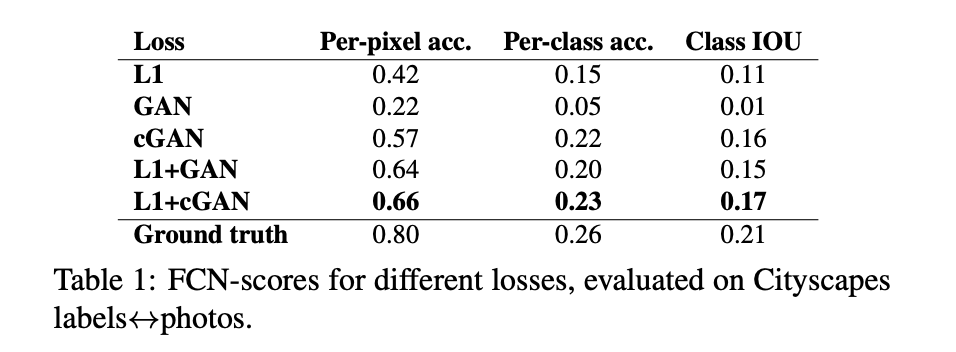
- cGAN이 GAN보다 더 좋은 performance를 보임
- 여기에 L1 Loss를 추가할 경우 더 성능이 향상됨
Analysis of the generator architecture

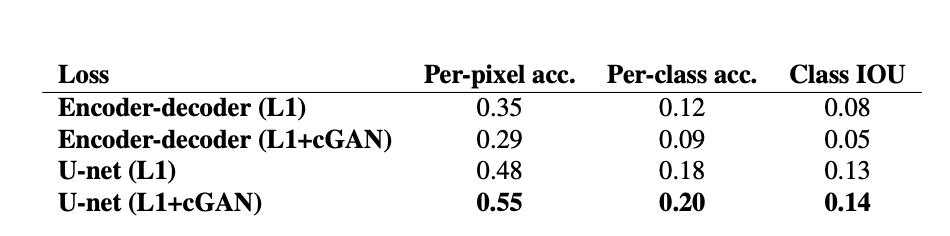
- Encoder-decoder 구조의 사용보다 Unet 구조 사용의 결과가 훨씬 좋다
- UNet architecture allows low-level information to shortcut across the network
From PixelGANs to PatchGANs to ImageGANs
-
패치 크기별로 실험을 진행, 1 : PixelGAN, 16x16 : PatchGAN, 70x70 : PatchGAN, 286x286 : ImageGAN

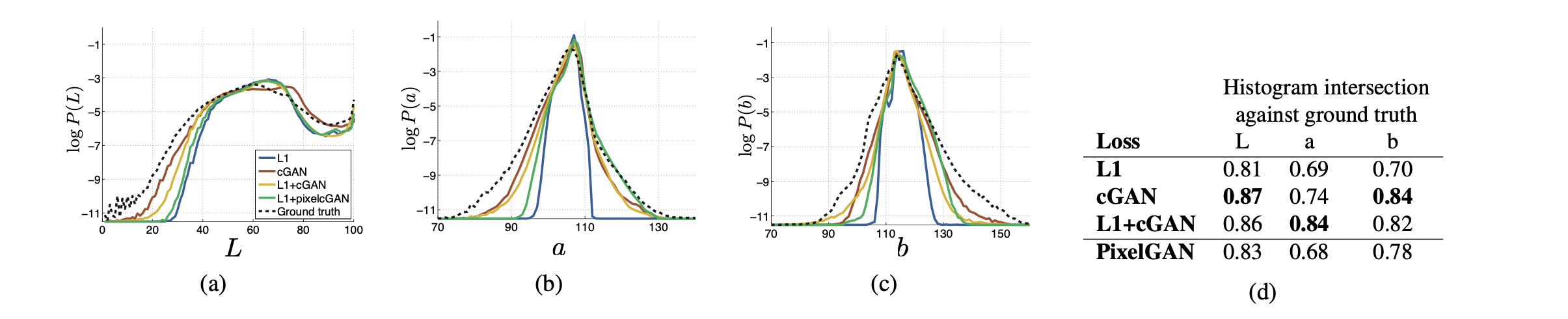
- 1x1 GAN은 L1 사용보다 color의 diversity가 높아졌으나, spaital statistic에는 큰 차이가 없음
- 16x16 GAN은 이전보다 sharp해졌으나, artifact가 나타나기 시작
- 70x70 GAN은 sharp하면서, 16x16의 artifacts 문제들을 개선함
- 286x286은 70x70 GAN보다 더 많은 파라미터와 깊은 깊이를 가져서 train 자체가 어려워지고, 따라서 성능 향상이 크게 이루어지지 않음
이외 결과들
Perceptual validation
- maps↔aerial 에서의 AMT 결과
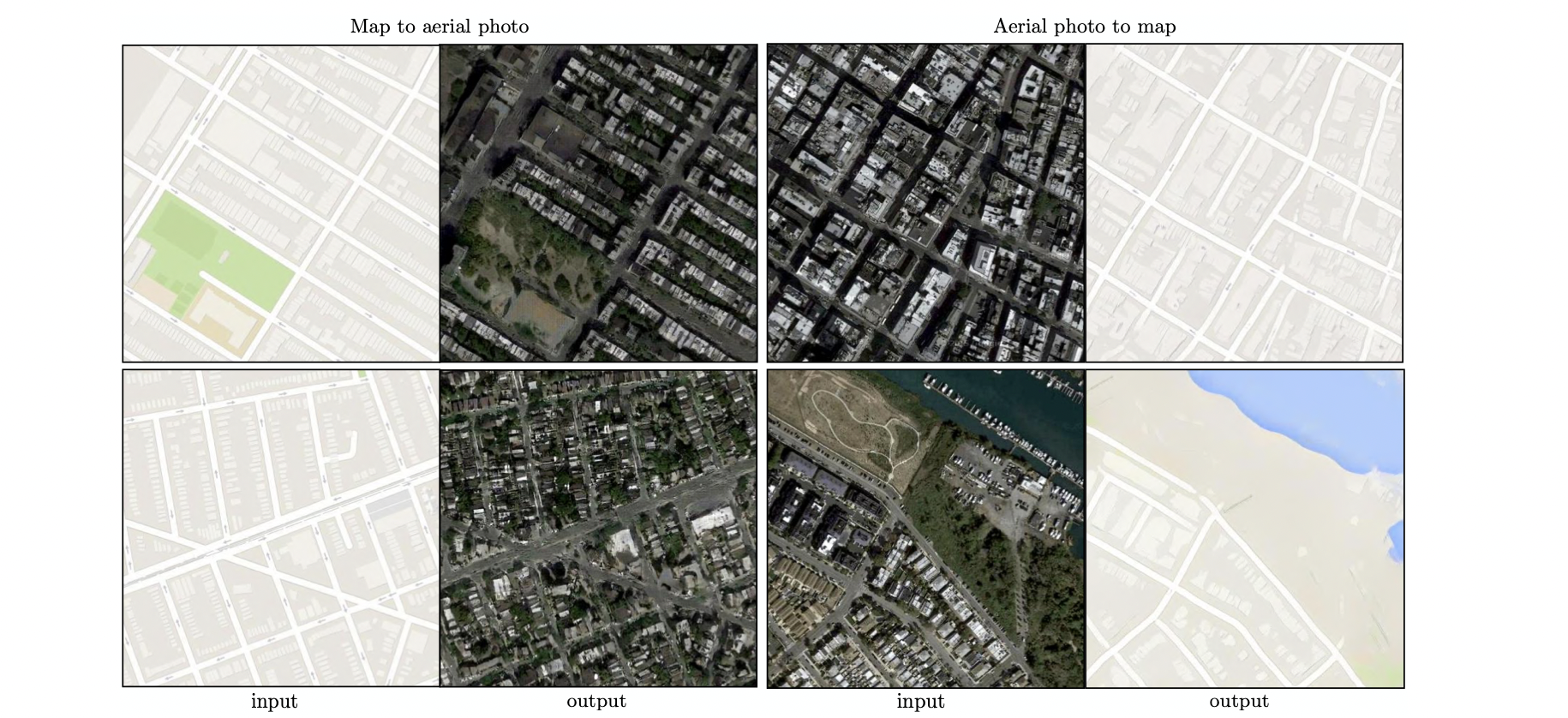

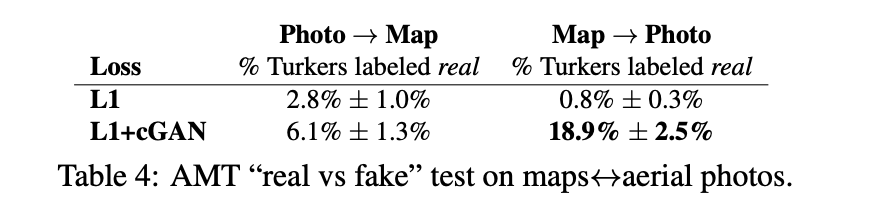
- map→photo의 경우 baseline인 L1보다 매우 많이 향상된 결과를 보여 주었음
- photo→map의 경우 baseline인 L1보다 크게 향상되지는 못함.
- may be because minor structural errors are more visible in maps, which have rigid geometry, than in aerail photographs, which are more choatic
-
colorization 결과
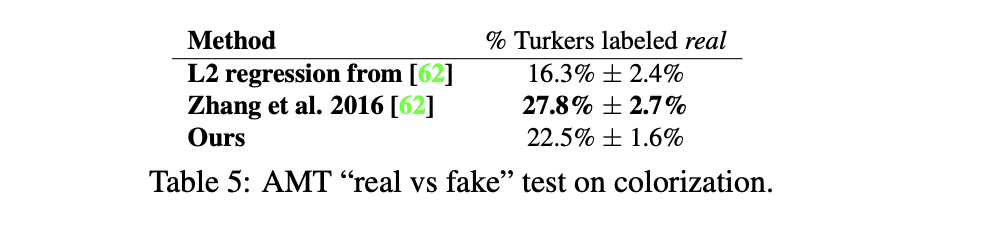
 Colorization은 특정 이미지에서 failure가 발생하기도 한다. colorization에 최적화된 네트워크는 아닌 것을 알 수 있다.
Colorization은 특정 이미지에서 failure가 발생하기도 한다. colorization에 최적화된 네트워크는 아닌 것을 알 수 있다. - Semantic segmentation
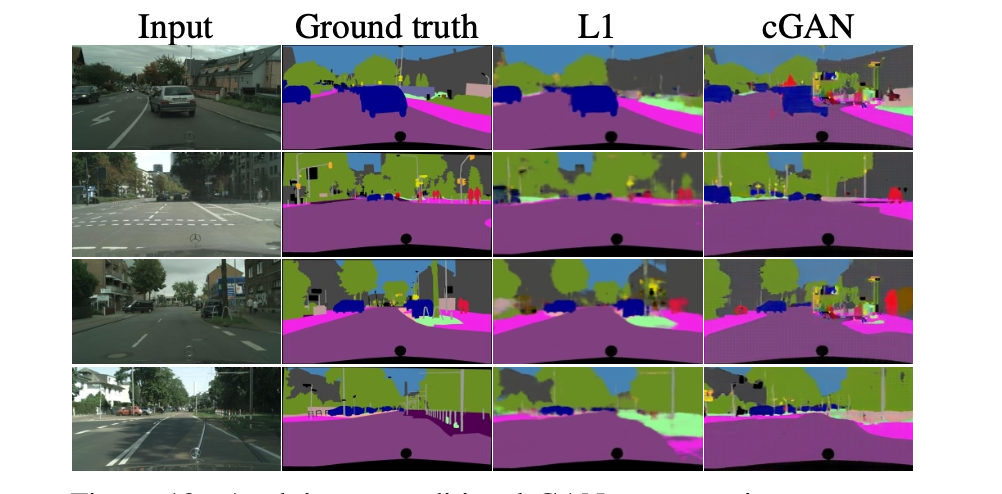
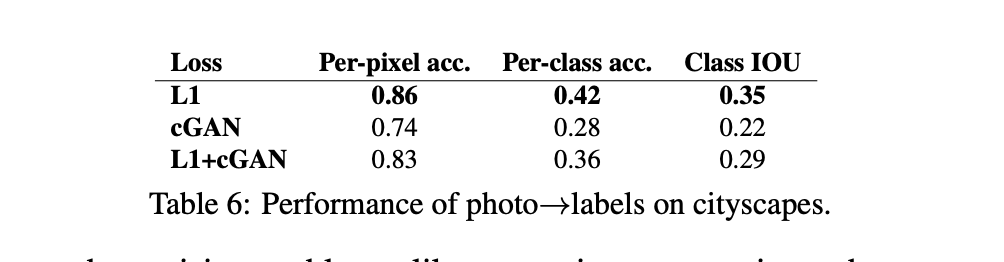
- cGANs trained without the L1 loss are able to solve this problem at a reasonable degree of accuracy → cGAN의 label generating에 적용하는 첫 시도
- simply using L1 regression gest better scores than using a cGAN
내가 생각했을 때, pix2pix는 오히려 aerial→map, 또는 segmentation과 같은 복잡하지 않은 이미지를 생성할 때는 적합하지 않아 보인다.
Discussion
- 여러가지 경우의 이미지 생성 문제를 하나의 Image-to-Image translation 케이스로 통합하여, 모두 적용 가능한 하나의 모델을 제안했다
- Generator에서 cGAN의 사용, UNet 구조의 적용과 discriminator에서 patchGAN의 적용, 마지막으로 L1 loss를 사용하여 성능 향상이 크게 이루어졌다.
여러 GAN모델들을 공부하고 나서 생각해보면, random noise z를 이용해서 generator와 discriminator로 이미지를 생성하는 GAN과는 살짝 다르게 문제를 풀어냈다고 생각할 수 있다. traditional pixel loss를 사용해서 모델이 deterministic하게 작동하도록 만든 게 paired에서는 되게 좋은 접근이라고 생각되나, 진정으로 conditional GAN이라고 말할 수 있는가? image condition을 모델이 받은 게 아니라 input으로써 image를 받아서 학습한 것이 아닌가 생각이 든다. 그치만 paired에서 되게 좋은 baseline임은 나도 인정한다!