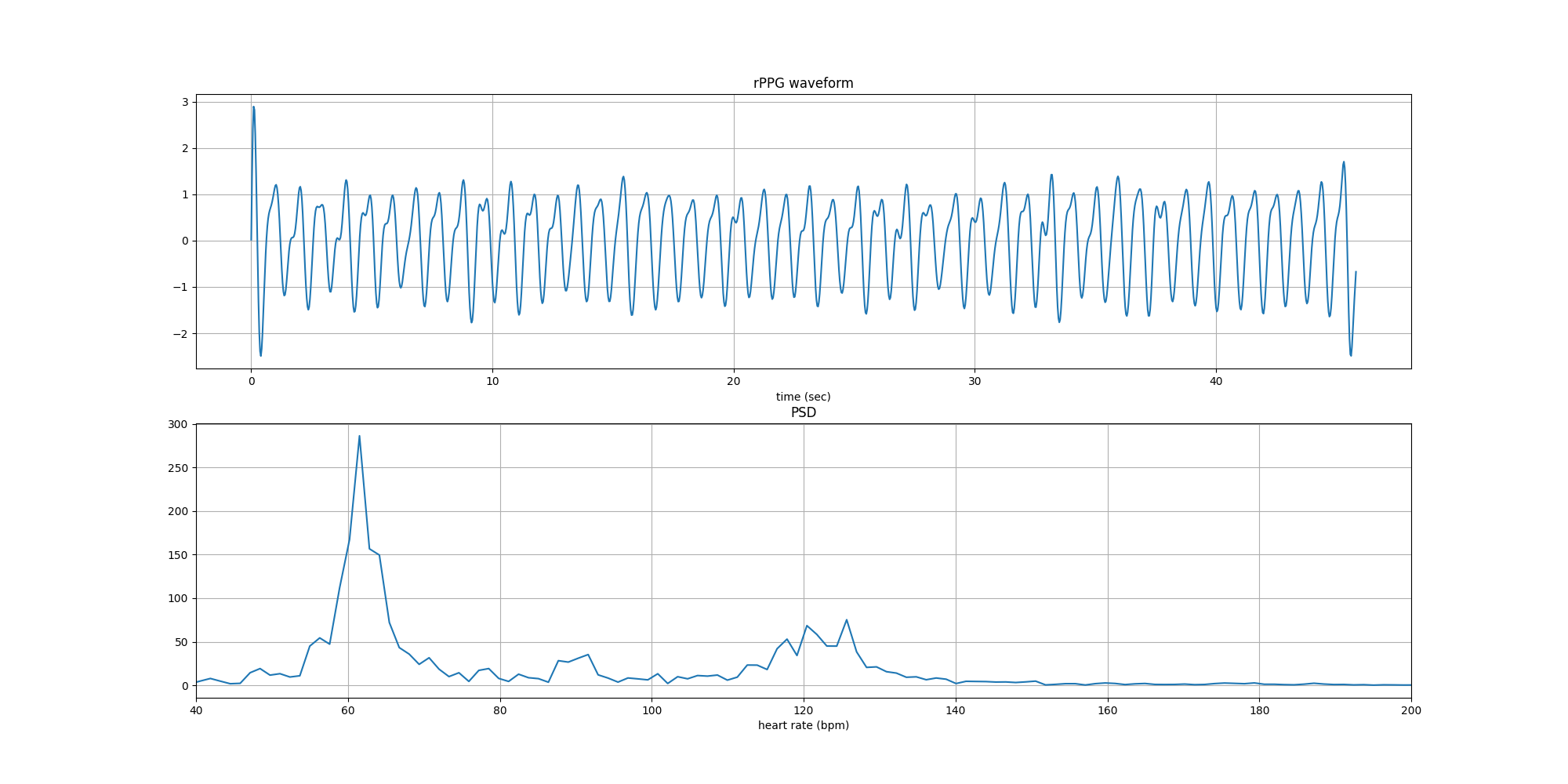
회사 인턴을 하면서 heart rate estimation을 해야 하는데 쓸만한 걸 못찾아서 잔뜩 스트레스 받고 있다가 찾은 모델이다. 트랜스포머 기반으로 해서 현재 SOTA 모델이다. 2D CNN기반은 거의 사용 못할 결과가 나오고, 대부분의 모델이 rPPG만 predict해서 실제 rPPG로 심박수를 계산해보면 처참한 수준의 결과만 얻을 수 있다. 그런데 이 모델은 rPPG에서 psd로 심박수로 추출하여 loss term에 활용하고 있기 때문에 심박수만 필요한 내 task에서 심박수가 쓸만한 정도로 나온다. 정말 한 줄기 빛의 모델이다.
배경지식 (ppg란?)
- 신체에서 얇은 부분(손끝, 볼, 귀)은 빛이 약간 통과 → 혈액의 흐름 관찰 가능
- 심장이 피를 보내기 위해서 뛸 때 생기는 미세한 변화 : 맥파, Plethysmogram
- 맥파에 따라 변하는 미세한 혈류량을 조사해서 파악.
PPG센서에서 피부로 빛을 쏠 때, 혈류량에 따라(심장이 이완 시 혈류량 증가, 수축시 혈류량 감소 ⇒ 심장의 이완, 수축 주기를 알 수 있음 ⇒ 심박수) 흡수되는 빛의 양이 달라지므로 빛이 얼마나 흡수되었는지를 측정하여 혈액량의 변화를 detect
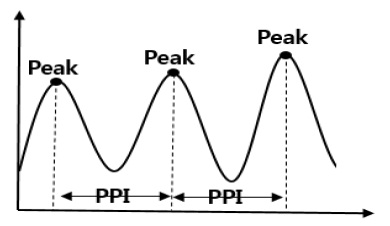
- 심박수 = \(1/PPI*60\)
- 반면 ecg는 심박동과 관련되어 나타나는 전위변화 (전기신호 세기와 간격)
rppg는 remote PPG로, facial video에서 얼굴의 혈류 변화량을 보고 ppg를 예측하는 방식
Introduction
Electrocardiography(ECG)와 Photoplethysmography(PPG)가 심장 활동을 측정하는 가장 큰 두 방식이다. 그러나 두 방식 모두 몸에 부착되어야 하는 불편함이 있기 때문에 remote Photoplethy-smography(rPPG) 가 떠오르고 있다.
3 stage module
보통의 rppg 연구는 3 stage를 띈다. paper
- a pre-processing stage, to minimize nuisance variation (face ROI 추출 및 전처리)
- detection + skin segmentation and tracking/ landmark
- 얼굴 이미지 추출이 얼마나 잘 되느냐가 rppg의 성능을 좌지우지 해서 초반에는 이쪽이 많이 발전
- ppg signal extraction stage
- ex. CNN
- a heart rate estimation stage from the estimated PPG signal (ppg를 bpm(heart rate)로 바꾸는 단)
- peak detection
- FFT (PSD)
가장 기본적인 방식
- analyze subtle color changes on facial regions of interest with classical signal processing approaches
그 다음 color 부분 처리를 통한 feature 맵 변환(color subspace transformation methods, which utilize all skin pixels for rPPG measurement)
위 방식을 바탕으로 ROI preprocess된 feature map에서 rppg를 추출하는 learning-based model 등장 (non end-to-end)
- ROI based preprocessed signal representations(e.g., time-frequency map and spatio-temporal map) are generated first, and then learnable models could capture rPPG features from these maps.
- 그러나 굉장히 strict하게 preprocessing 요구
아예 processing된 feature map이 아닌 video 자체를 input으로 받는 end-to-end 모델들이 등장
- treat facial video frames as input and predict rPPG and other physiological signals directly
- 그러나
- 전처리단이 사라졌으므로 complex scenarios(e.g, head movement)에서 무너져내리는 경향이 있음
- rPPG-unrelated feature가 학습에 주 부분을 차지할 가능성 → large performance decrease in realistic dataset
- 전처리단에서 정제+증폭해줬던 부분이 없으므로 ppg추출 단이 훨씬 어려운 task로 바뀜
ppg → Heart rate
-
보통 모델 output이 ppg 추출에서 끝나는 모델이 많다
→ heart rate 변환 시 noise 제거 등 signal processing이 또 필요할 수도 있음
- dl based이 아닌 traditional 방법론을 사용
- fft(PSD), peak detection
- 그래프 개형이 비슷한 것(mse)과 주기(bpm=heart rate)가 비슷한 것은 다르다고 생각!
- heart rate를 loss term에 사용하지 않는 이상 ppg 그래프보다도 heart rate가 실제와 많이 다른 경우가 존재
Transformer의 사용
- rppg에서도 CNN based 모델이 대거 등장
- NLP, image / video analysis에서도 성공적으로 작동했으므로 rppg에서도 적용할 수 있을 것
- 기존과 다른 점은, subtle한 픽셀 변화에 의존하기 때문에 global spatio-temporal perception이 challenging
- the long-range spatio-temporal attention이 필요
- rPPG measurement from facial videos can be treated as a video sequence to signal sequence problem
- LONG RANGE contextual clues should be exploited for semantic modeling
Contribution
- powerful video temporal difference transformer backbone으로 이루어진 physformer 모델의 제안
- long-range spatio-temporal relationship을 고려한 첫 rppg model
- PhysFormer의 supervise 방법론들 제안
- label distribution learning
- curriculum learning guided dynamic loss in frequency domain
- pretrain 없이 SOTA 달성
Related Works
Remote physiological measurement
Plenty of traditional hand-crafted approaches
Face input에서 feature map 추출 단:
- Selective merging information from different color channels / different ROIs
feature map에서 rppg 추출 단:
- to improve signal-to-noise ratio of the recovered rPPG signals, several signal decomposition methods such as independent component analysis(ICA), and matrix completion이 제안
Learning based approach의 등장
-
deep learning based approaches dominate the field of rPPG measurement due to the strong spatio-temporal representation capabilities.
- not end-to-end (facial ROI 전처리단 + rppg 추출단)
- facial ROI based spatial-temporal signal map 생성 단:
- alleviate the interference from non-skin regions
- ROI 전처리가 꽤 많은 비중을 차지
- ROI 바깥 부분을 전혀 고려하지 못함(배경 밝기 변화 같은)
- map들에서 feature를 잡아내는 rppg단 (2D-CNN)
- 실시간성에는 좋음
- 따라서 spatial-temporal 정보들을 고려하기가 힘듬
- facial ROI based spatial-temporal signal map 생성 단:
- end-to-end
-
인접한 프레임만 고려하고 long range relationship의 주기적인 정보는 고려하지 않음
(previous methods only consider the spatio-temporal rPPG features from adjacent frames and neglect the long-range relationship among quasi-periodic rPPG features)
-
Transformer for vision tasks
Most of these works are incompatible for long-video-sequence (over 150 frames)
rppg in vision transformer
- trans-rppg
- extracts rPPG features from the preprocessed signal maps via ViT for face 3D mask presentation attack detection
- efficientphys (temporal shift networks)
- Based on the temporal shift networks, efficientphys adds several swin transformer layers for global spatial attention
위 두 모델은 non-end-to-end모델 (feature map에서 rppg 추출 단)
Materials and Methods
PhysFormer Architecture.
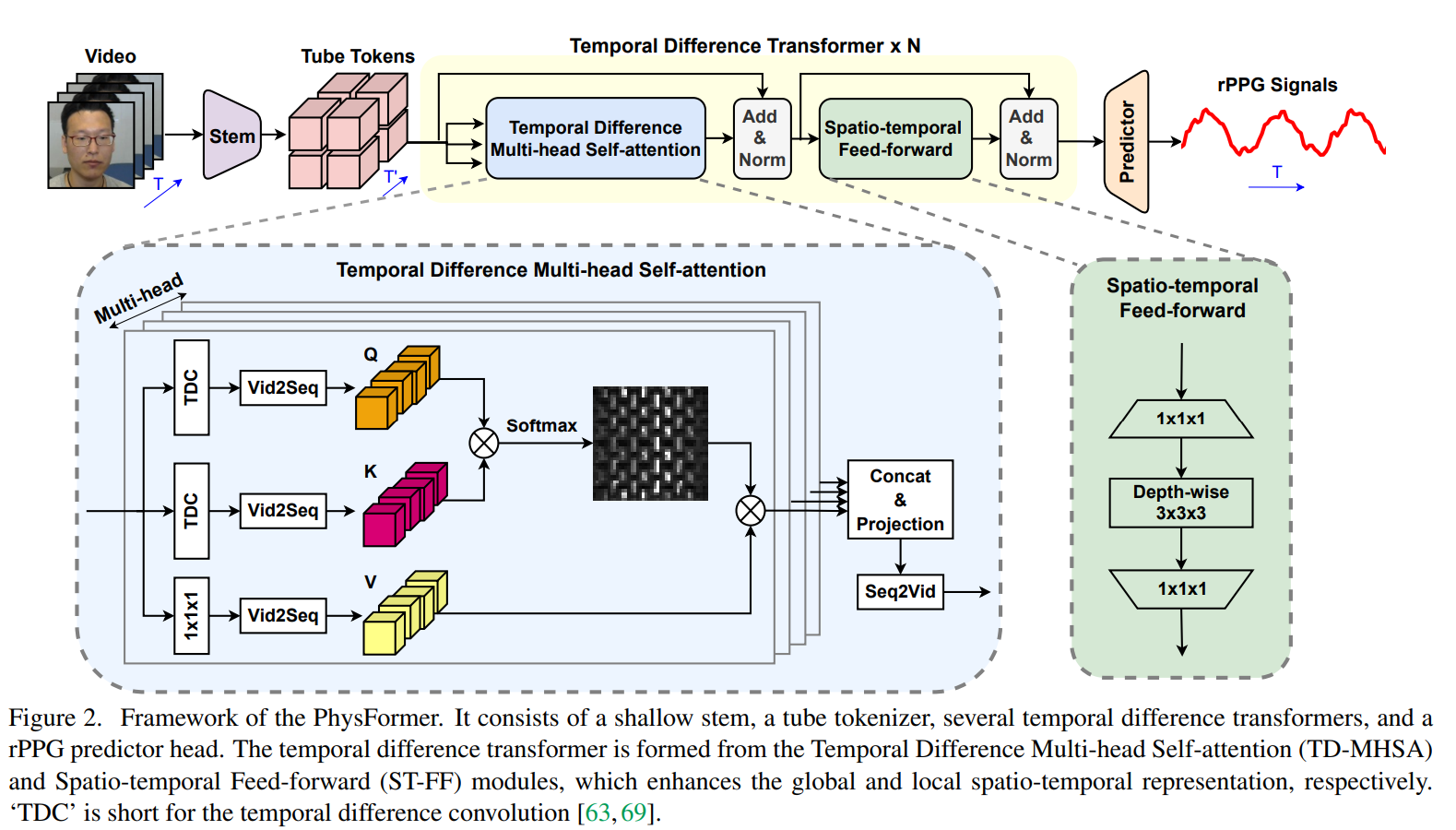
Shallow stem
- Video를 바로 patch로 쪼개서 multi head self attention에 넣는 것이 아니라 얇은 stem을 한번 거친 output을 patch로 쪼개서 MHSA에 넣음
- coarse한 local spatio-temporal feature 추출에 도움
- benefits the fast convergence and clearer subsequent global self-attention
- 3개의 convolution blocks이루어져 있다 (커널 사이즈: 1x5x5, 3x3x3, 3x3x3)
- 각 convolution에 Batch Normalization, ReLU, MaxPool을 순차적으로 사용
- Pooling layer가 spational dimension을 반으로 나누므로
- Facial video input size가 3xTxHxW 일때 shallow stem output size는 D x T x H/8 x W/8
Tube tokenization
- 이 shallow stem의 output이 N개의 tube token으로 나뉘어지고, 이렇게 나뉘어진 tube token들이 N개의 temporal transformer block으로 들어가고, global-local refined rPPG 피처인 X_trans을 얻을 수 있다. (X_tube와 동일한 dimension)
- stem에서 나온 output을 X_stem이라고 할때, X_stem을 non-overlapping한 tube token들로 나뉘어진다.
- stem이 있으므로 position embedding과정을 따로 진행해주지 않았다.
Temporal difference multi-head self-attention
- AutoHR 논문에서 등장한 temporal difference convolution 개념
- 기존의 self attention은 Query, Key, Value를 단순히 matmul 해주는 형태(1x1 conv)
- matmul (point-wise linear projection) 하는 대신 Temporal difference convolution을 사용
- 동영상의 밝기와 같은 값들을 인접한 프레임끼리 빼줌으로써 무시 가능
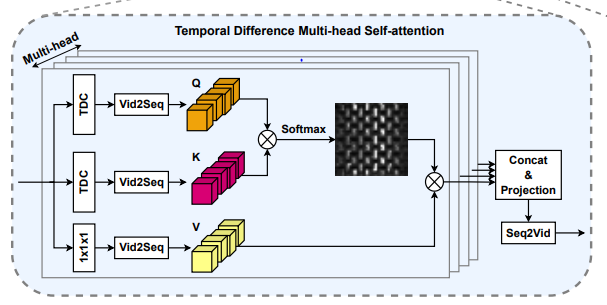
- 동영상의 밝기와 같은 값들을 인접한 프레임끼리 빼줌으로써 무시 가능
- TDC with learnable w
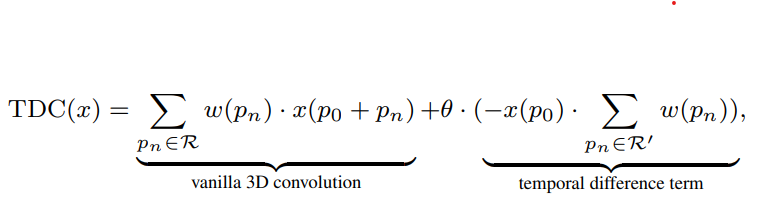
p0 : current spatio-temporal location, R : sampled local (3x3x3) neighborhood, R’ : sampled adjacent neighborhood
-
temporal difference convolution을 Q(query)/K(key)의 projection에 사용.
⇒ 미묘한 색 변화 감지를 위해 미세 특징을 포착할 수 있음 (can capture fine-grained local temporal difference features for subtle color change description)
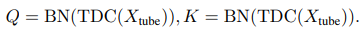
- V(value) projection 때에는 temporal difference convolution projection을 사용하지 않고 기존의 point-wise linear projection을 사용
i번째 head의 self-attention:
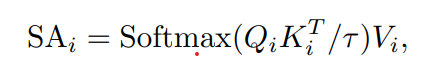
- 기존의 self-attention식처럼 τ =√Dh_i를 사용한 것이 rppg에서 효과가 좋지 못했으므로, 더 작은 τ를 사용해 sharper attention activation을 진행. (변수로 받아서 진행)
- 여기에 residual connection, layer normalization이 마지막으로 진행된다.
Spatio-temporal feed-forward
-
TD-MHSA의 output이 피드포워드 NN의 input FFNN(x) = MAX(0, xW1+b1)*W2+b2 (두개의 linear 층)
- vanilla feed-forward network
- 두개의 linear transformation layer로 구성
- 두 레이어 사이에서 더 많은 feature 표현을 위해서 hidden dimension이 확장됨 (the hidden dimension D’ between two layers is expanded to learn a richer feature representation)
- temporal한 정보 고려가 힘듬
- depthwise 3D convolution(with BN and nonlinear activation)을 이 두 레이어 사이에 사용
- ST-FF가 local inconsistency와 parts of noisy features를 다듬어 줄 수 있다고 제안
- richer locality는 TD-MHSA에게 충분한 relative position 신호를 제공
Label Distribution Learning
Facial age estimation task에서, 나이 차이가 적을수록 얼굴이 비슷해보이는 점을 이용
⇒ Facial rPPG signals with close HR values usually have similar periodicity.
- 하나의 얼굴 video에 대한 output이 하나의 label(HR)이기보다는, label distribution을 이용해 output이 여러 개의 HR value label에 대한 distribution으로 표현되도록 함.
- label distribution은 HR의 특정 범위(42, 180)을 포함하고, output은 각 label들이 얼마나 유력한지에 대한 정도를 표현함.
- Through this way, one facial video can contribute to both targeted HR value and its adjacent HRs.
💡 rPPG-based HR estimation problem을 specific L-classes multi-label classification problem으로 정의했다. (L=139, 42 to 180)
GT label을 어떻게 label distribution으로 만들었는가?
- 각 label의 entry p는 [0,1] 사이의 real value이고, 모든 label의 p 합은 1이 되도록 했다. (확률)
- Gaussian distribution function을 이용
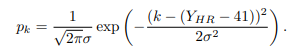
-
오히려 real distribution을 사용했을 때보다 gaussian distribution을 사용했을 때 더 성능이 괜찮았다!
- 결국 loss function은 L_LD = KL(p, Softmax(ˆp)) 나타낼 수 있다. KL은 Kullback-Leibler divergence이고, p hat은 power spectral density(PSD) of predicted rPPG signals. ⇒ rppg에서 HR 추출을 어떻게 했는지를 알려주고 있음
- Kullback-Leibler divergence - 두 확률분포의 차이를 계산하는데 사용하는 함수 (정보 엔트로피 차이를 계산)
- Power Spectral density(PSD)
이전에도 label distribution을 이용한 사례(A robust rppg approach with distribution learning)가 있었지만, 우리와 차이점은
- 이전에 이 방식을 사용한 이유는 frame마다의 얼굴 움직임에 대해 temporal HR outliers를 smoothen하는 것이지만, 우리는 adjacent label간의 efficient feature를 배우도록 하기 위해 진행하였다.
- 이전 연구에서는 hand-crafted rppg signal 추출 이후에 HR-estimation를 위한 post HR estimation이지만, 우리는 딥러닝 단에서 적용하였다.
Curriculum Learning Guided Dynamic Loss
- Curriculum Learning - 쉬운 task부터 학습
temporal domain loss
- mean square error loss, negative Pearson loss
- negative Pearson correlation : maximize the trend similarity and minimize peak location errors (Remote Photoplethysmograph Signal Measurement from Facial Videos Using Spatio-Temporal Networks에서 등장한 loss)
- signal-trend-level constraints을 주므로 금방 학습 → 쉬운 overfitting
frequency domain loss
- cross-entropy loss, signal to noise ratio loss
- target frequency bands에서 주기적인 피처들을 학습해야 함
- realistic한 rPPG-irrelevant 노이즈 때문에 주파수단의 강한 constraints
이게 중요하다. frequency domain loss가 심박수를 loss term으로 활용할 거라는 말이기 때문에 rPPG prediction에서만 잘 작동하는 것이 아니라 heart rate estimation에서도 잘 작동할 수 있게 된다.
또한, dynamic supervision to gradually enlarge the frequency constraints를 제안.
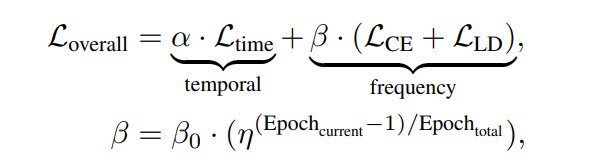 linear increment strategy/exponential increment strategy 중 exponential strategy를 적용 (alpha = 0.1, beta_0 = 1.0, n = 5.0)
linear increment strategy/exponential increment strategy 중 exponential strategy를 적용 (alpha = 0.1, beta_0 = 1.0, n = 5.0)
- pretrain을 사용하면 HR로만으로도 학습 가능할 수도 있을 것 같다!! 지금 가지고 있는 rPPG 데이터가 없어서 한 줄기 빛이 된다.
Results
세개의 physiological signal에 대해 진행 :
heart rate(HR), heart rate variability(HRV), respiration frequency(RF)
사용한 데이터셋
VIPL-HR
- large-scale dataset for remote physiological measurement under less-constrained scenarios
- head movement, illumination을 포함
- 2378 RGB videos of 107 subjects recorded with different head movements, lighting conditions and acquisition devices
MAHNOB-HCI
- one of the most widely used benchmark for remote HR measurement evaluations
- 527 facial videos with 61 fps from 27 subjects
MMSE-HR
- 102 RGB videos from 40 subjects
OBF
- high-quality dataset for remote physiological signal emeasurement
- 200 5 min ong RGB videos with 60 fps recorded from 100 healthy adults
- mean HR estimation은 위의 네개 데이터셋에서 진행
- HRV, RF estimation은 OBF에서만 진행
- follow existing methods, and report low frequency(LF), high frequency(HF), and LF/HF ratio for HRV and RF estimation
- SD, MAE, RMSE, pcc(peason’s correlation coefficient)
Implementation Details
- MTCNN face detector을 이용하여 첫번째 프레임의 enlarged face area를 crop, 이후 frame들도 이 region으로 fix
- MAHNOB-HCI, OBF는 fps=30으로 내렸음
- Physformer 세팅 :
- N=12, h=4, D=96, D’=144,
- TD-MHSA : θ=0.7 (for TDC), τ=2.0
- tube size T_s x H_s x W_s = 4x4x4
- train시에 randomly sample RGB face clips with size 160x128x128(TxHxW)
- Random horizontal flipping and temporally up/down-sampling for data augmentation
- Adam optimizer
- lr = 1e-4, weight decay = 5e-5
- batch size=4
- 25 epoch으로
- alpha=0.1 for temporal loss,
- exponentially increased parameter beta=[1,5] for frequency loss.
- σ=1.0 for label distriution learning (gaussian distribution)
- testing : seperate 30-second videos into three short clips with 10 seconds, and video-level HR is calculated via averaging HR from three short clips
Intra-dataset Testing
HR estimation on VIPL-HR
- traditional methods(Tulyakov2016, POS, CHROM) perform poorly due to the complex scenarios
- end-to-end learning based methods(PhysNet, DeepPhys, AutoHR) predict unreliable HR values with large RMSE compared with non-end-to-end learning approaches(PhythmNet, ST-Attention, NAS-HR, CVD, Dual-GAN)
- all five non-end-to-end methods first extract fine-grained signal maps from multiple facial ROIs, and then more dedicated rPPG clues would be extracted via the cascaded models.
- Physformer는 pretrain 없이도 좋은 결과를 낸다!
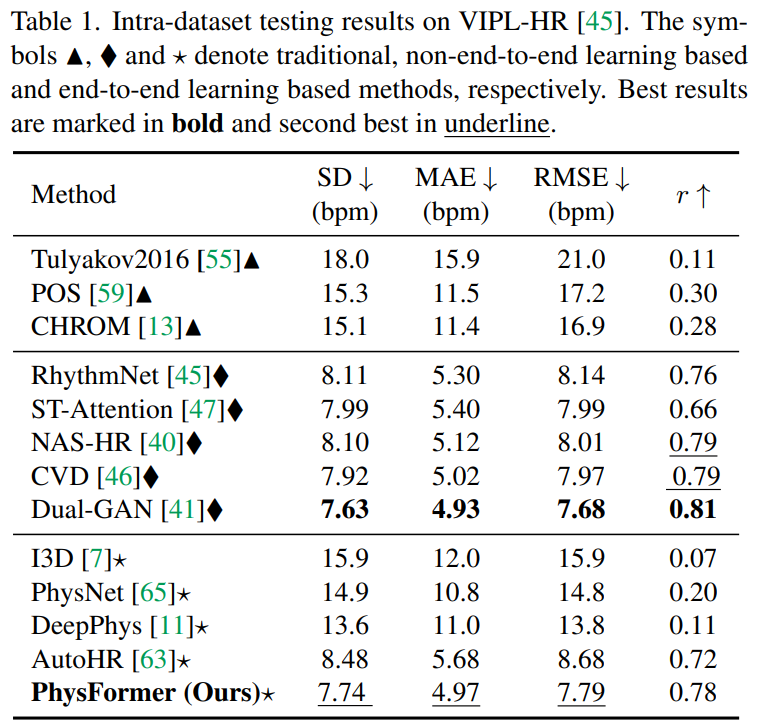
HR estimation on MAHNOB-HCI
- finetune the VIPL-HR pretrained model on MAHNOB-HCI for further 15 epoc
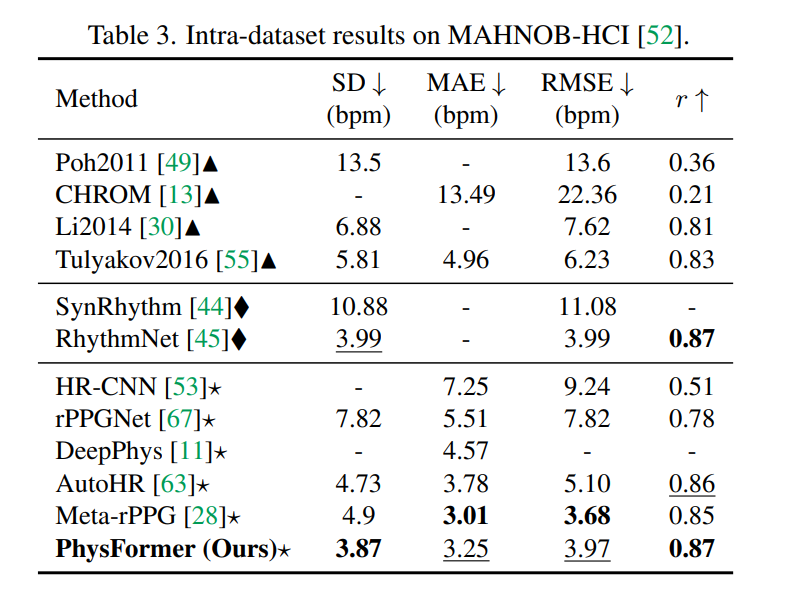
HR, HRV and RF estimation on OBF
Physformer also gives more accurate estimation in terms of HR, RF, and LF/HF compared with the preprocessed signal map based non-end-to-end learning method CVD.
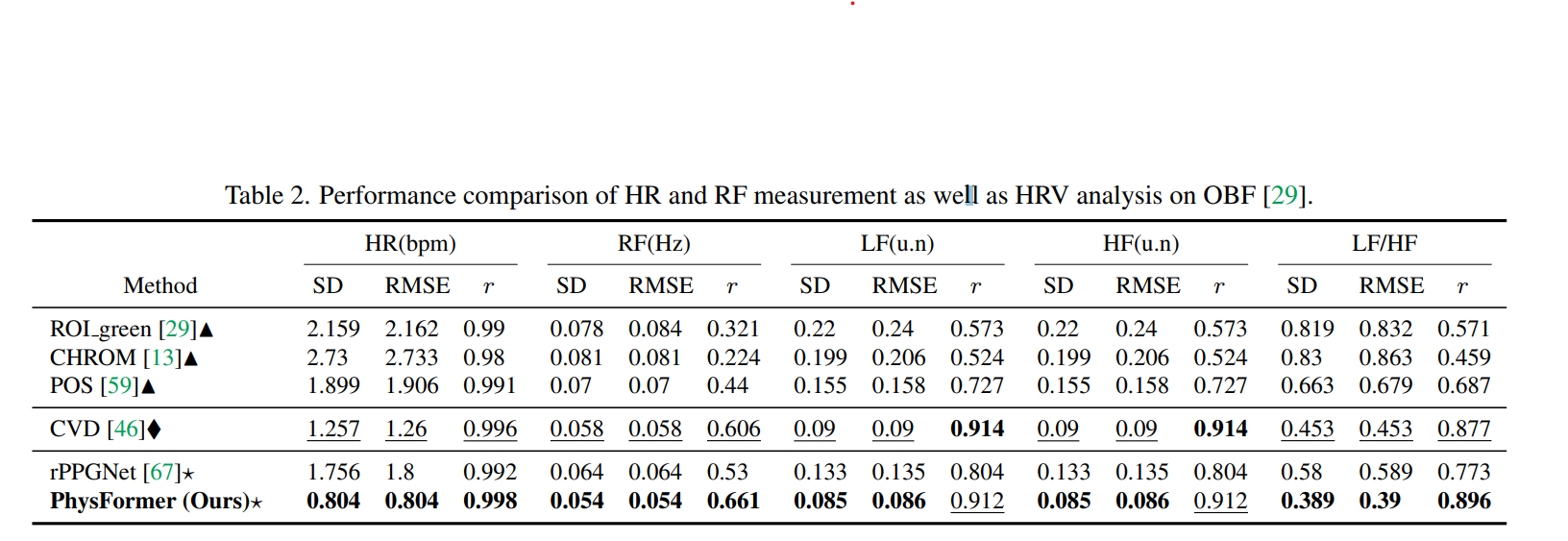
Cross-dataset Testing
- VIPL에 train 후 MMSE-HR에 finetune 하지 않고 바로 testing
- SOTA 달성
- The predicted HRs are highly correlated with the ground truth HRs
- The model learns domain invariant intrinsic rPPG-aware features.
Ablation Study
Impact of tube tokenization
four tokenization configuration 유무
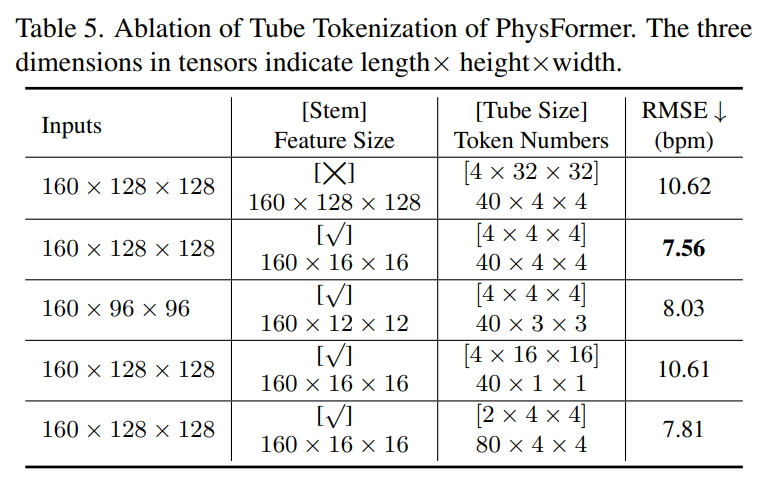
- stem을 사용했을 때가 더 결과가 좋았음
- input resolution을 내릴수록 결과가 안좋아짐
Impact of TD-MHSA and ST-FF
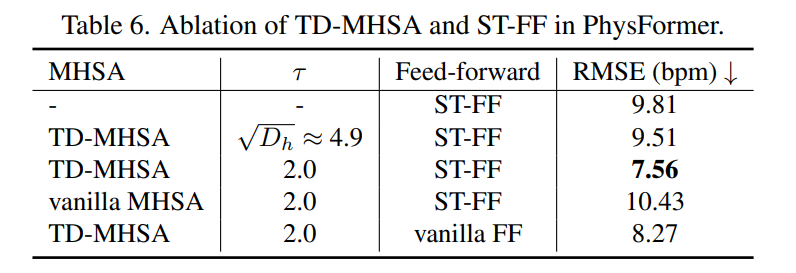
- Spatio-temporal attention 없을 때 performance degrades sharply
- τ가 MHSA에 영향을 많이 준다 ⇒ ViT처럼 타우를 사용하면 성능 drop
- ViT보다 τ를 작게 잡았을 때(sharp) 성능이 더 향상 되었다.
Impact of label distribution learning
Impact of dynamic supervision
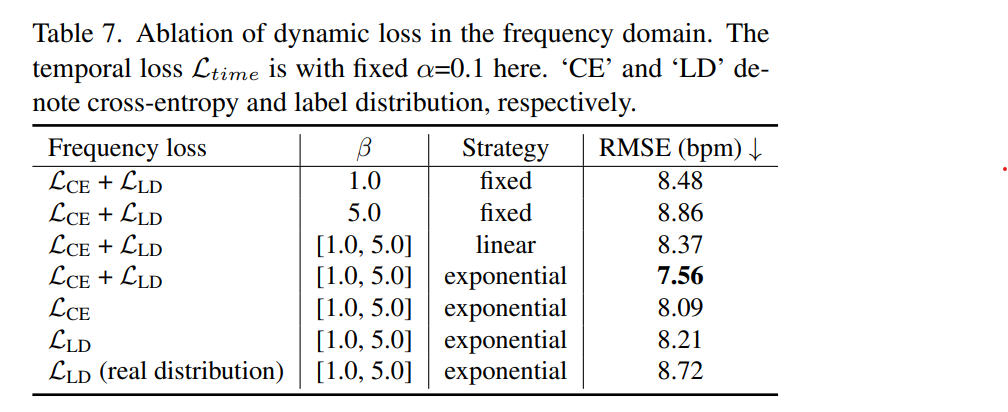
- Temporal loss와 frequency cross-entropy loss에서, frequency loss쪽이 label distribution
- label distribution을 exponential strategy로 사용했을 때 가장 결과가 좋음
- label distribution을 아예 사용하지 않았을 때는, exponential strategy를 적용해도 결과가 좋지 않았음
- It is interesting to find from the last two rows that using real PSD distribution from ground truth PPG signals as p, the performance is inferior due to the lack of an obvious peak and partial noise. (real PSD distribution보다 가우시안 distribution이 더 좋았다)
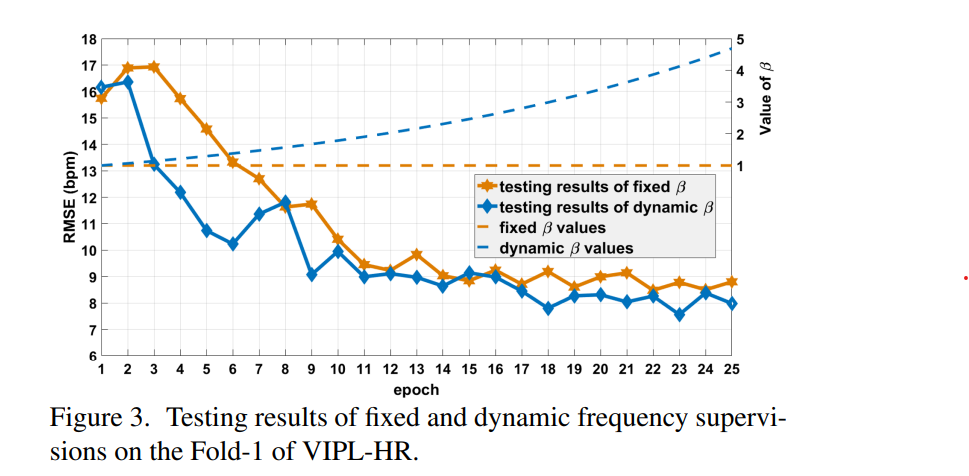
- Fold-1 VIPL-HR로 fixed/dynamic supervision을 실험하였을 때
Impact of theta and layer/head numbers
Physformer could achieve smaller RMSE when theta=0.4 and 0.7, indicating the importance of the normalized local temporal difference features for global spatio-temporal attention.
With deeper temporal transformer blocks, the RMSE are reduced progressively despite heavier computational cost.
In terms of the impact of head numbers, it is clear to find that PhysFormer with four heads perform the best while fewer heads lead to sharp performance drops.
Conclusion
- rppg를 위한 End-to-end video transformer architecture를 만듬
-
Temporal difference transformer를 사용한 성능 향상
- 더 효율적인 architecture
- 모바일에서는 사용하기 어려운 parameter 수
- More accurate yet efficient spatio-temporal self-attention mechanism for long sequence rPPG monitoring
rPPG라는 게 얼굴에서 사람의 눈으로 감지하기 어려운 혈색의 변화를 감지해서 ppg 그래프를 그려야 하는 문제이기 때문에, 이게 진짜 가능한거냐라고 말하는 사람들도 있고 나도 어느 정도는 동감한다. 그래서 많은 rPPG 추출 모델들이 이 subtle한 혈색 변화를 증폭시킬 수 있는 모듈을 사용하는데 여기서는 그게 TDC였던 거다.
그런데 직접 physformer 실험을 해보면 30fps에서는 잘 작동하더라도 frame interpolation으로 fps를 바꿔줬을 때 잘 작동하지 않는다. 이게 모델이 30 fps에서만 주로 학습이 되어서 일수도 있지만, 내가 생각하기에는 모델이 프레임 간의 차이(temporal difference)를 보고 있다기보다 그 순간의 혈색이 얼마나 붉은지를 보는, temporal 정보를 고려하고 있지 않을 수도 있는 것 같다. 사람 혈색이 얼마나 빠르게 주기적으로 변하냐보다도, 특정 프레임에서 사람 얼굴이 붉으면 이 사람이 운동 중이라고 생각하고 높은 심박수를 뱉는 경향성이 있다. 그래서 인종에 대한 bias도 많이 걸리고, 아무튼 참 어려운 문제이다.