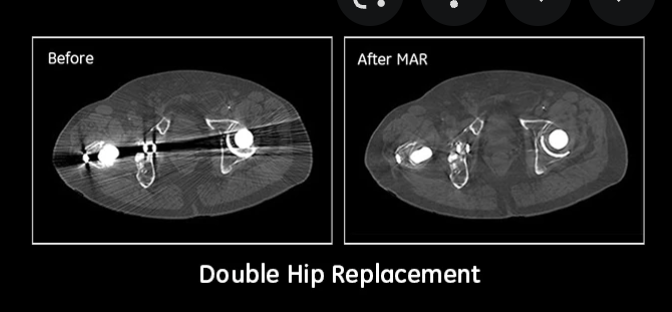
이번에는 내가 하고 있던 metal artifact reduction에 대한 논문 리뷰이다! MAR은 이미지 postprocessing이랑 preprocessing으로 나눠져서 이미지 도메인을 쓰는 방법론이랑, 사이노그램 도메인을 쓰는 방법론 이렇게 두개가 있는데, 여기서는 사이노그램 도메인을 이용하여 metal artifact를 지웠다!
Introduction
→ The presence of dense materials, such as metals, can strongly attenuate or even completely block X-rays, producing severe streaking artifacts in the FBP reconstruction.
CT를 촬영하면 1차적으로 사이노그램 이미지가 나오게 되는데, 이것을 다시 CT image로 reconstruction을 하기 위해서 FBP(Filtered back projection)이라는 방법을 사용하게 된다. 그런데 이때 CT 안에 dense material이 존재 시 streaking artifact를 만들고, 이는 이미지 품질에 매우 치명적이다. 그래서 metal artifact reduction(MAR)를 하는 여러 방법론들이 제안되고 있는 것이다.
The standard practical approaches to reducing metal artifacts in CT imagery are either simplistic nonadaptive interpolation-based projection data completion methods or direct image post-processing method, which had limited success. traditional method such as interpolation-based projection data completion methods(지워진 부분에서 중간값을 취하는 방법) 등이 잘 못하므로, 딥러닝을 이용한 방법론을 활용하는 추세가 점점 늘어나고 있다.
⇒ This paper aims to reduce metal artifacts in CT images by applying deep learning(DL) directly in the projection-domain, prior to image formation. (우리는 따라서 딥러닝을 이용한 MAR 방법을 제안하고, 이것은 image formation 전에 projection-domain에서 이루어질 것임.)
Materials and Methods
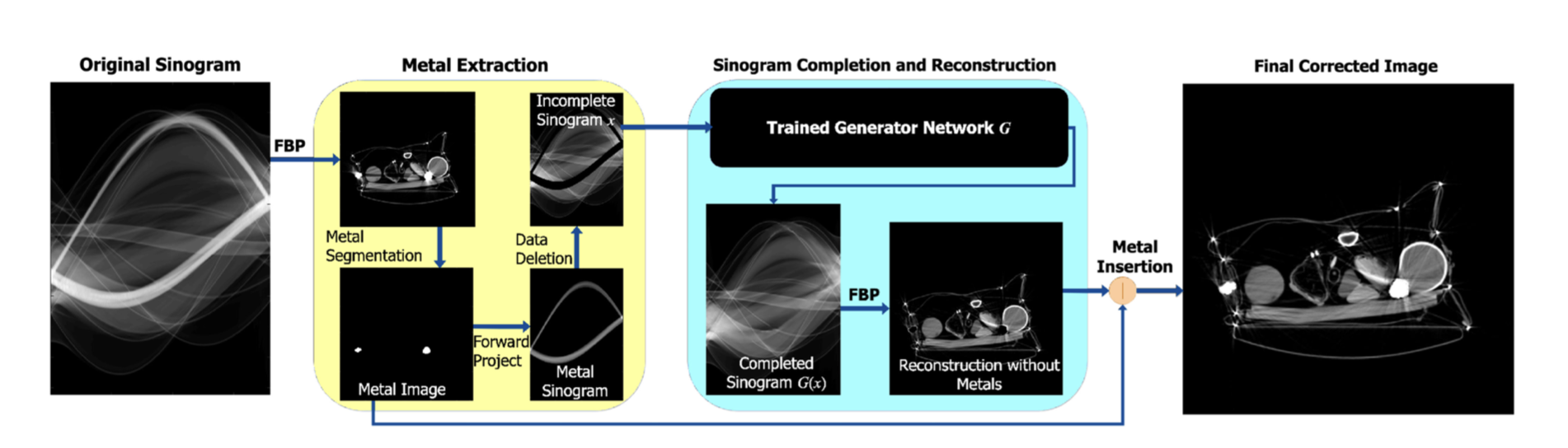
identification and suppression of metal-contaminated projection data
 In order to identify the metal-contaminated projection data a conventional FBP reconstruction using th eoriginal sinogram is first generated.
In order to identify the metal-contaminated projection data a conventional FBP reconstruction using th eoriginal sinogram is first generated.
Thresholding followed by morphological operations are then used to segment the metallic objects in the image, which are forward projected to generate a mask, M.
(Thresholding이 사용되었고, morphological operation(erosion, dilation)이 후처리에 이용된다) mask가 generate ⇒ inpainting 모델의 적용 가능성
mask는 실제 metal부분보다 조금 더 크게 설정하여, 모든 artifact를 확실히 지우도록 했다.
cGAN based sinogram completion
overall mini-max objective function:
x: input (incomplete-data), y: ground truth (true complete-data sinograms) Discriminator loss의 포함이 l2 only loss를 사용했을 때 비해 전체적인 결과를 향상시켜주었다. 또한 두번째 term에서 l1 loss의 사용보다 l2 loss의 사용이 더 좋은 performance를 보여주었다.
LcGAN(G, D):
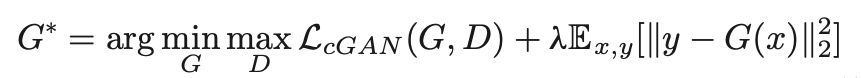 Ex : expectation over incomplete data density, approximated by averaging over input training data samples x.
Ex : expectation over incomplete data density, approximated by averaging over input training data samples x.
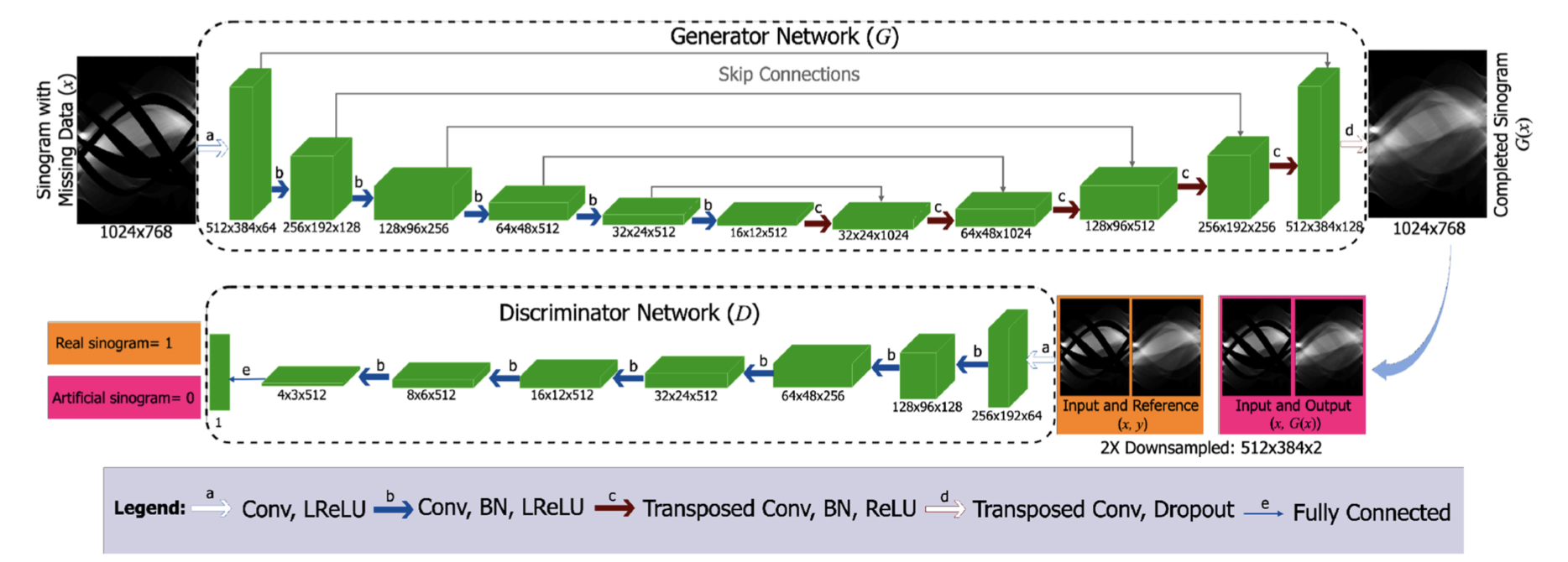
Generator
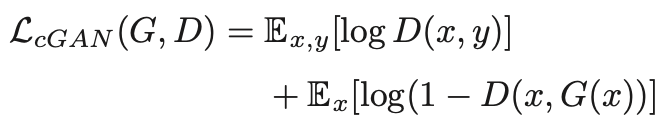 modified U-Net architecture with a fully convoluiontal architecture가 사용되었음.
modified U-Net architecture with a fully convoluiontal architecture가 사용되었음.
- U-Net의 skip connection 사용, layer i와 layer n-i를 concat하는 방식.
Convolutional kernels of size 5x5 with a stride of 2 are used at each layer for both the generator and discriminator networks.
Down-sampling에서 max-pooling대신 two-pixel strided convolutions를 사용
Up-sampling에서는 transposed convolutions with two-pixel strides가 사용됨.
Overall 6 downsampling and 6 upsampling layer를 사용
stride-2 convolution이 stride-1 convolution과 비교했을 때 훨씬 큰 practical effective receptive field(ERF)를 제공함 https://arxiv.org/pdf/1701.04128.pdf ⇒ 여기서 ERF 개념이 소개됨.
Receptive Field : 각 단계의 입력 이미지에 대해 하나의 필터가 커버할 수 있는 이미지 영역 theoretical ERF는 layer수와 함께 증가
- 6 downsampling layer와 6 umsampling layer에서는 theoretical ERF가 757x757 ⇒ 굉장히 큰 sinogram도 handle
Kernel size또한 ERF에 근거하여 설정되었음.
- smaller kernels would require more layers to achieve a desired ERF
- larger kernels would result in many more learning parameters needing estimation
- Empirical testing showed that 5x5 convolutional kernels with a shallower architecture perform better than 3x3 convolutional kernels with a deeper architecture.
Dropout이 overfitting을 방지하기 위해 마지막 layer에 사용되었음. (BN 다음에)
Discriminator
based on the full sinogram image, instead of just patches
- Missing data follows sinusoidal structure, which would not be possible to accurately capture using a patch-based discriminator (missing data부분이 사인파 형태를 띄기 때문에 patch기반 discriminator가 형태를 정확히 잡아내기 어렵다)
By using mask-specific sinogram completion our loss function is focused on the areas of most interest - where the data is missing. (loss function이 mask부분만 맞추도록 element-wise multiplication을 진행) generator network output is given by : G(x) = x + M ⊙ x_D1 (x_D1 : the output of the last layer of the generator network, M : the metal mask, ⊙ element-wise multiplication)
⇒ Inpainting
efficient FBP image reconstruction and reinsertion of metal objects back into the reconstructed image
- Model의 output인 complete-data sinograms에 FBP를 진행 ⇒ 우리가 아는 CT image가 생성
- FBP 이후의 이미지에는 metal위치가 뚫려 있음. 따라서 metal object의 reinsertion 진행
Dataset Generation
- Transfer Learning (전이 학습)
- In the security domain there is a great diversity of possible objects in a scene, yet the amount of physical CT data avilable for training is severely limited.
- To address this limitation, we generated a training set for sinogram completion using physically accurate X-ray simulation tools.
- After initinal training, our networks are then refined with available physical data through transfer learning.
- Areas without metal are considered background(air) in this work. This approach makes the problem more tractable since the network can focus on a smaller space of possibilities. (메탈이 없는 부분은 air로 간주, 따라서 네트워크가 더 작은 가능성에 집중할 수 있다. ⇒ 메탈이 있으면 티슈 외의 메탈 부분을 맞추기 위해서 모델이 메탈에 더 집중.)
Simulated Training Data Generation
1) Physically accurate X-ray scanner model
We can accurately model the data obtained from such scanners as a sum of mono-engergetic sinograms weighted by the corresponding relative strength of the source spectrum.
I_(i): relative X-ray source intensity at enery E(i), I_j(i): Sinogram contribution at engergy E(i) for ray-path j corresponding to the line Lj(Beer-Lambert law사용)
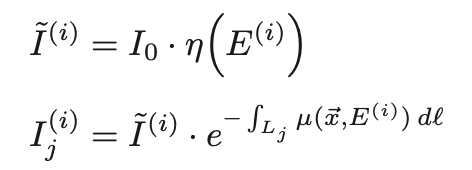
- The projection data contributions are degraded by data-dependent and electronic noise ⇒ Poisson distribution, Gaussian zero-mean으로 표현
- By incorporating a full energy aware x-ray model, effects such as beam hardening are inherently included. (Beam hardening과 같은 효과도 연출이 가능하다.)
2) Stochastic bag simulator This bag or scene simulator places objects of different material composition(티슈 부분을 랜덤으로 표현) and of varying geometric configuration at random locations in the scene.
uses material attenuation coefficients drawn from the NIST XCOM database.
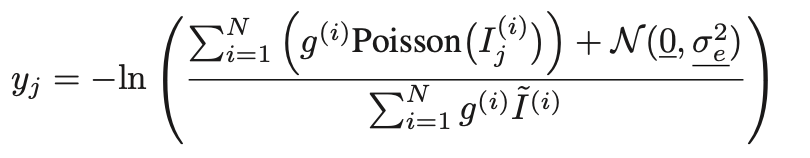
Real Training Data Generation
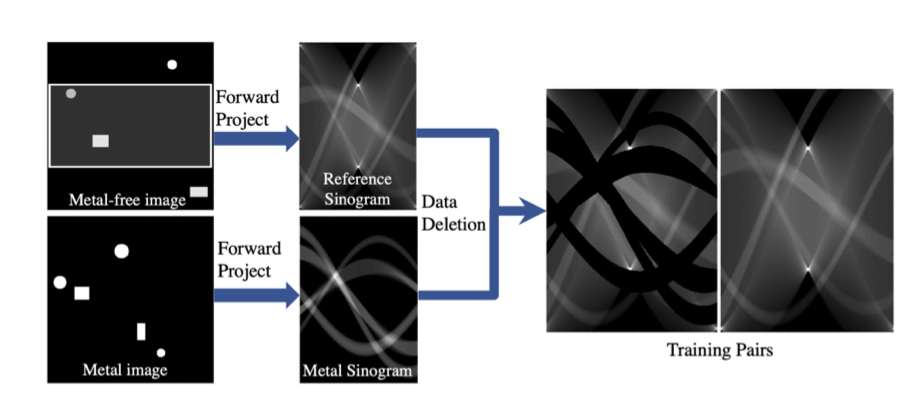
- Acquiring physical matched sinogram pairs with and without metal objects for training is a challenge
- Our approach only requires metal-trace masked and corresponding metal-free complete sinograms for CGAN training since we are focusing our learning on missing data completion. (우리의 방식은 단순히 metal mask와 metal이 없는 사이노그램 이미지이므로, 실제 전체 Metal 이미지를 얻을 필요가 없다.)
- We can use sinogram data from scenes which do not contain metal objects, and then create matched sinograms by deleting data in the sinogram that corresponds to geometric configurations of embedded objects. ⇒ metal이 없는 clean한 sinogram에서 geometric configurations 부분만 간단히 삭제하면 됨. (꼭 metal이 있는 이미지가 필요 없음!)
- metal mask identified by applying a threshold of 4000 Modified Hounsfield Units(MHU = 1000 + -1000(μ-μ_water)/μ_water. p Threshold mask results were eroded(used to remove very small objects) and dilated with a disk-shaped structuring element of radius 2 and 4 pixels respectively to obtain a final metal mask.
Result
LI-MAR와 WNN-MAR와 우리 DeepMAR가 비교되었고, simulated data와 real data 모두에 대해 진행되었다.
Sinogram Completion Experiments
(a)가 simulated data, (b), (c)가 real data.
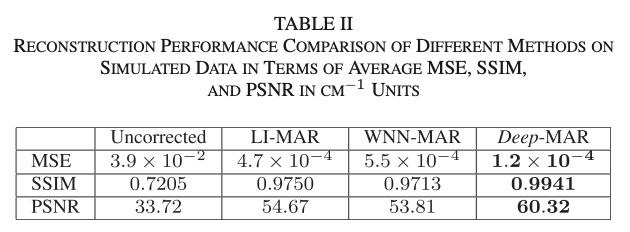
- simulated data에 대해 LI-MAR와 WNN-MAR에 비해 각각 89%, 87% 더 MSE가 적었음.
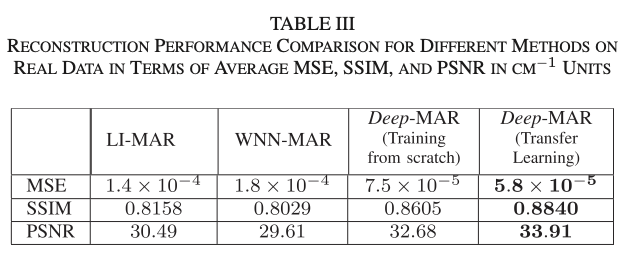
- real data에 대해 80%, 75% 더 MSE가 적었음.
- Transfer learning을 사용했을 때 31% 정도의 성능 향상이 있었다.
Simulated Data Reconstruction Experiments
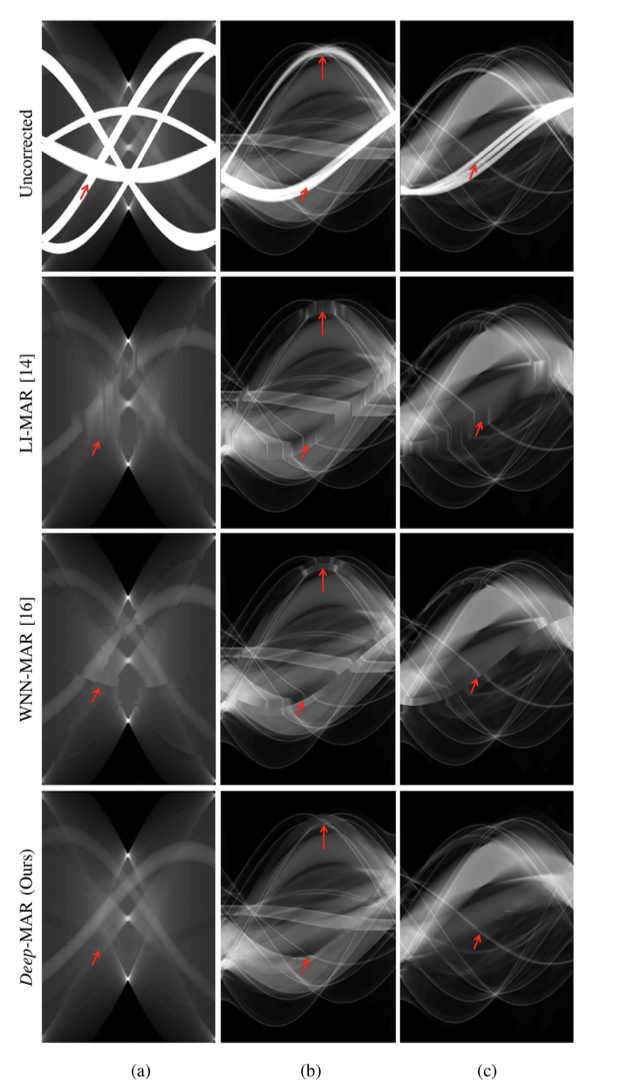
- Deep-MAR에서 모두 결과가 매우 향샹되었음. artifact가 가장 잘 제거된 모습을 볼 수 있음.
- SSIM, PSNR의 향상이 의미하는 것: Deep-MAR approach not only performs well in qualitatively suppressing metal artifacts, but is also good at correcting the underlying attenuation values, and correct attenuation numbers are important for the successful functioning of security algorithms.
- (metal artifact를 눈으로 봤을 때 잘 줄이는 것 뿐만 아니라, 감쇠된 부분을 잘 맞춘다는 것을 의미 ⇒ 다른 security algorithms의 작동에 있어서도 중요 (진짜 데이터 같다는 의미)
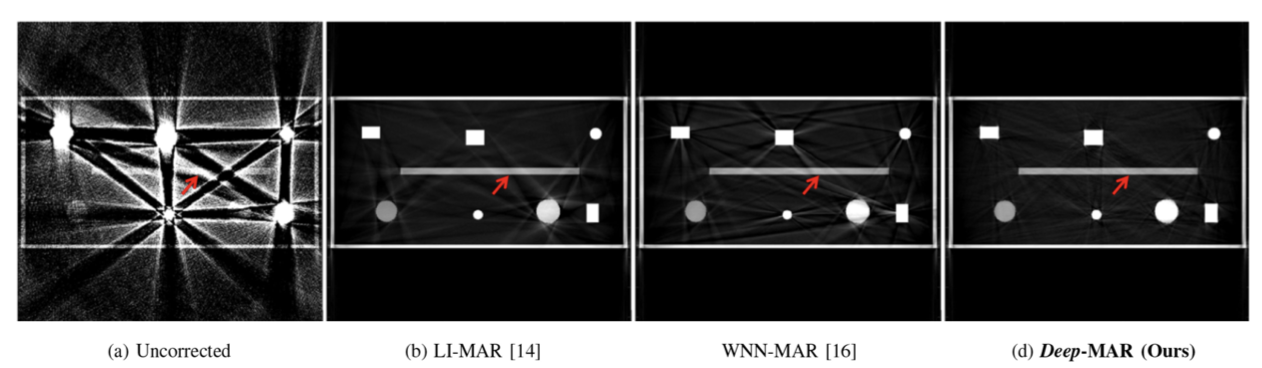
Real Data Reconstruction Experiments
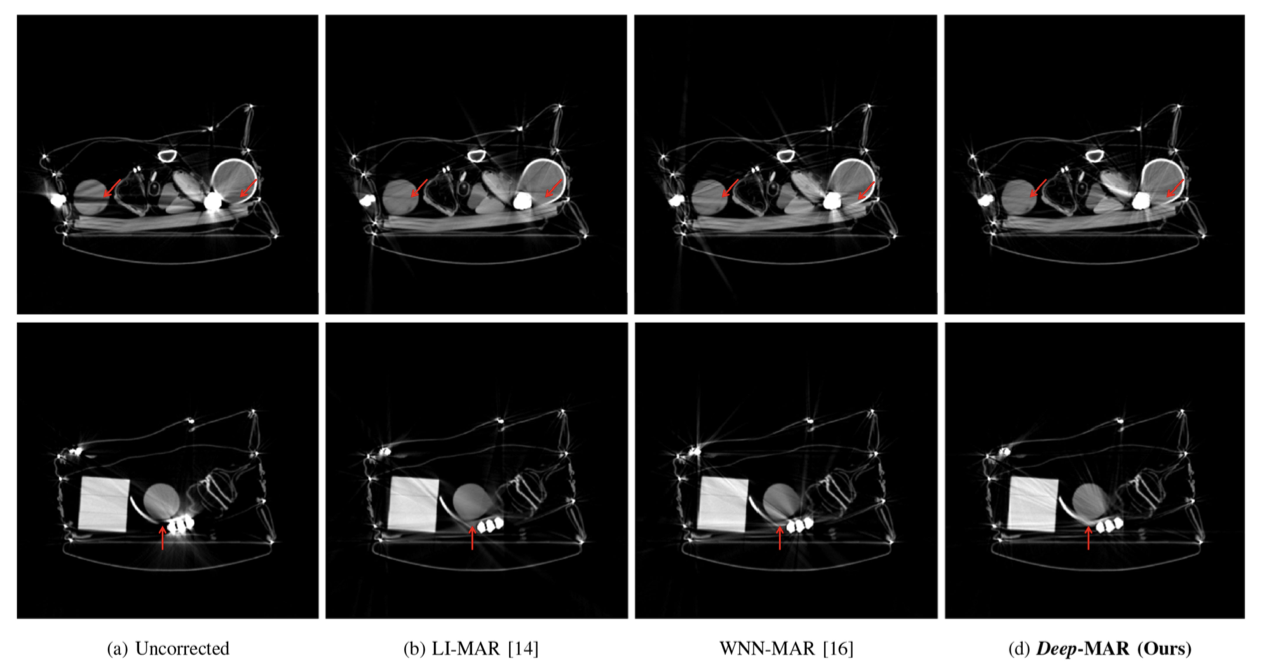
 기존의 방법들은 오히려 streak artifact가 생겨나는 경우도 존재하지만, Deep-MAR는 가장 자연스럽게 채운 것을 볼 수 있음
기존의 방법들은 오히려 streak artifact가 생겨나는 경우도 존재하지만, Deep-MAR는 가장 자연스럽게 채운 것을 볼 수 있음
Attention Maps
Zeiler and Fergus의 Image to Image translation 연구에서 사용한 방법인데,
- Compute attention maps by occluding different regions of the input image and examining the resulting impace on performance of the deep network on the corresponding image classification task.
- The idea is that occlusion of more important image areas to the network will correspondingly have greater resulting performance impact.
- In this work, we apply this idea by repeatedly replacing an 11x11 patch of sinogram values with random data sampled from a uniform distribution U(0, m) and then examining the resulting sinogram completion performance.
- (11x11 patch의 사이노그램 값들을 U(0, m)으로 바꿔치기후, performance가 어떻게 바뀌는지를 조사)
- We then compute the corresponding MSE for the sinogram regions completed by learned network and generate a 2-D attention map by associating this MSE value with the center of the corresponding noise patch.
- (해당하는 region의 MSE를 계산 후, 이 MSE value와 해당 noise patch에 대한 2-D attention map을 그렸다. Metal artifact reduction은 gt가 없어서 평가가 매우 어려운데, 이러한 식으로 모델이 mask안을 채울 때 주변 픽셀들을 얼마나 참고하고 있는지를 visualize하여 성능 평가를 할 수 있는 척도 중 하나로 사용한 것이다.
모든 그림에서 metal mask 주변의 attention이 강하게 나타나는 것을 볼 수 있다. (pixels closest to the missing data appear to be the most important in generating an estimate, which seems logical)
(a), (b)는 메탈이 하나일때의 결과, (c), (d)는 메탈이 5개 일 때의 결과(challenging)이고, (c), (d)에서 전체적인 attention map의 수치가 높아진 것을 확인 가능하다.
Discussion
따라서 논문의 contribution은 두개 이다.
MAR 문제에 대해 Deep-MAR라는 DL-based framework를 제안하였다. 그리고 딥러닝에서 발생하는 training data 확보 문제를 해결하기 위해, transfer learning을 활용한 방법론이다. 이때, simulated training data에서 학습 후 (얼마 없는) real data에서 transfer learning을 함으로써 성능을 확보하였다.