블로그에 AI 관련 포스트는 안하고 있었는데, AI 대학원 진학을 하기로 마음을 먹고 난 후라, 그동안 노션에 정리해두었던 논문들을 하나씩 포스트하면서 내가 공부한 것들을 정리해보려고 한다. **날짜는 논문을 읽었던 날짜순으로 포스팅된다.
Introduction
computer vision의 큰 두 분야에는 patch matching using low-level image features (ex. PatchMatch) 와 feed-forward generative models with deep convolutional networks (ex. Ours)로 이루어진다. 즉 딥러닝을 사용하지 않는 단순한 traditional 방법론이 앞에 속하고, 딥러닝을 사용하는 CNN 네트워크가 후자에 속한다.
Vanilla convolution
vanilla convolution은 우리가 알고 있는 평범한 CNN을 말하는 것이다.
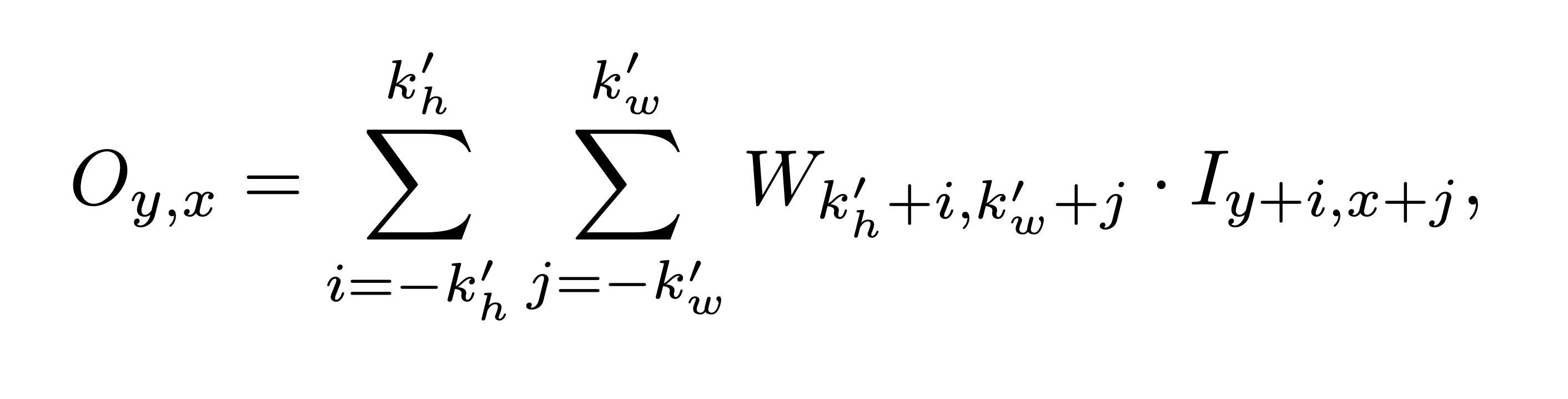 kh, kw : kernel size. kh’=(kh-1)/2, kw’=(kw-1) W: convolution filter I: Input, O: Output
kh, kw : kernel size. kh’=(kh-1)/2, kw’=(kw-1) W: convolution filter I: Input, O: Output
- 공유된 convolution filter들은 모든 pixel & feature를 valid 하다고 생각하고 처리해버린다.
- 따라서 mask가 없는 image classification, object detection에서 문제 없이 작동한다. 즉, 모든 pixel이 valid한 경우에 문제없이 작동한다.
- 그러나 mask가 있는 task의 경우 valid한 픽셀에 대해서만 처리를 할 수 있도록 convolution을 변경해 주어야 한다. valid한 픽셀에 대한 구분 없이 처리하게 되면
→ leading to visual artifacts such as color discrepancy, blurriness and obvious edge reponses surrounding holes when tested on free-form masks.
⇒ partial convolution이 제안된다.
Partial convolution
- adapts a masking and re-normalization step to make the convolution dependent only on valid pixels
- followed by rule-based mask-update step to update valid locations for next layer
- 0-1 mask를 모든 input에 곱한다 (viewed as a single un-learnable feature gating channel) wmr hole이 mask된 부분으로 0, non-hole은 1.
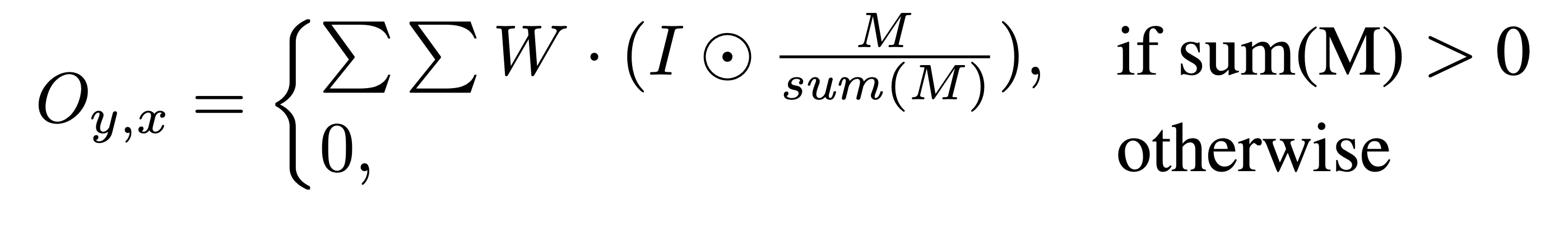
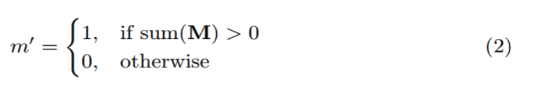
- convolution을 진행 할 때 따라서 non-hole인 부분이 아주 조금이라도 있으면 계산, 모두 hole이라면 0을 부여
- UNet based 방법론
- 총 6개의 Loss (L_valid + 6L_hole + 0.05L_perceptual + 120(L_style_out + L_style_comp) + 0.1 L_tv)를 사용
partial convolution의 limitation
- It heuristically classifies all spatial locations to be either valid or invalid. (경험적으로 분류)
- 따라서 다음 mask를 업데이트 할 때, filter 영역 안에 valid한 픽셀이 몇개가 있던 모두 1로 설정이 된다.
- User-guide를 도입했을 때, 이 픽셀들은 valid인가 아니면 invalid인가?
- User-guide와 같이 새로운 특징을 도입했을 때 0, 1 둘중에 하나로 binarize하기 어려워진다.
- “Invalid” pixels will progressively disappear layer by layer and the rule-based mask will be all ones in deep layers.
- 다 채워지지도 않았는데 이미 mask는 모두 1이 되어버리는 현상 : 모든 픽셀이 valid하다고 생각해버리게 된다.
→ We will show that if we allow the network to learn the mask automatically, the mask may have different values based on whether current locations are masked or not in input image, even in deep layers.
- All channels in each layer share the same mask
- which limits the flexibility
즉 partial convolution을 정리해보면, un-learnable single-channel feature hard-gating이라는 점이다. (hard-gating은 값이 0, 1 두개로만 결정되는 것을 말함) 따라서 저자는 Gated convolution을 제안하는데,
Gated convolution
- learns a dynamic feature gating mechanism for each channel and each spatial location
- formulation
- input feature는 먼저 gating value g = σ(wgx)에 들어가 계산된다. (σ : 시그모이드, wg : learnable parameter)
- 최종 output은 learned feature와 gating value의 곱으로 표현되고, 여기에 activation function을 씌워준 것이 된다.
- mask가 arbitrary shape일 때, 아니면 input이 심플한 RGB 채널이 아닌 conditional inputs를 가지고 있을 때 굉장히 잘 작동한다. (결국 user-guide를 수용한다는 의미)
Materials and Methods
Gated Convolution
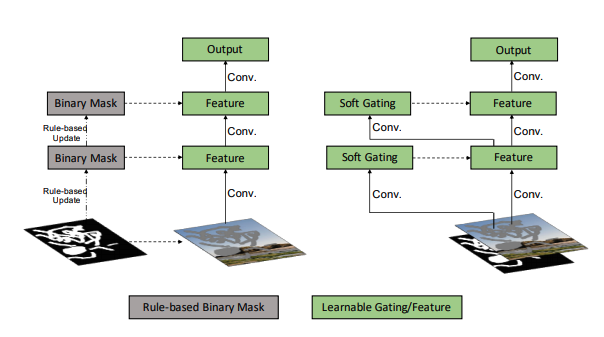 partial convolution의 경우 binary mask가 단순히 rule-based update된다.
partial convolution의 경우 binary mask가 단순히 rule-based update된다.
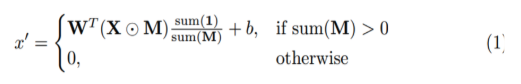

- 그러나 gated convolution을 보면 mask가 soft gating을 통해(0,1 둘만의 값으로 밀리는 hard gating이 아닌) 업데이트됨.
-
soft gating 과정

- convolution layer가 sigmoid를 거친 것으로 mask가 업데이트됨.
- 0, 1사이의 값으로 나오게 되고 이것은 validness를 의미하고 있다고 볼 수 있다.
- soft mask와 feature를 element-wise product 진행하여 valid에 가까울수록 더욱 큰 attention이 들어가도록 연산 (dynamic feature selection mechanism)
SN-PatchGAN
- 이전의 rectangular mask가 아닌, free-form mask를 처리하기 위해 고안됨.
- motivated by global and local GANs, MarkovianGANs, perceptual loss, spectral-normalized GANs
Marchovian Discriminator
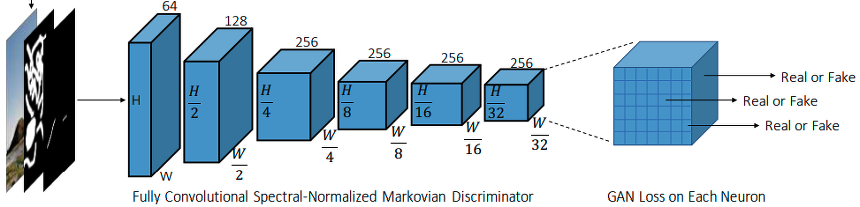
- kernel size 5, stride 2인 여섯개의 convolution network가 feature statistics of Markovian patches를 잡는다.
- 여기에 GAN을 바로 적용 → R^(h * w * c) 의 GAN이 만들어짐.
그럼 Markovian patches가 뭔가?
- Markovian GANs - GAN의 계산적 효율성 이슈를 해결하기 위해 생김
-
deep generative model을 full-image models와 deep Markovian models로 구분(local patches의 통계만을 잡음)
- 기존의 방법들은 deconvolution과 feature activations(higher network layer)의 pre-image( pixels)를 추정하기 위해 역전파 요구가 굉장히 커서 run-time cost가 굉장히 컸다.
- 이것을 해결하기 위해 strided convolution network를 inversion process에 맞춰서 network의 inversion을 미리 계산하는 방법!!!
- strided convolution 연산을 통해 feature statistics를 잡음. strided convolution 연산을 feed forward 한 것이 feature 통계를 잘 잡기 때문에 이러한 구조를 사용
deepfillv1에 있는 local discriminator와 global discriminator에서 왜 global discriminator가 사라졌는가?- 각 뉴런의 receptive field가 전체의 Input image를 커버할 수 있다.
Spectral Normalization
- Weight normalization 중 하나
- Lipschitz 상수 하나만을 hyperparameter로 가짐
그럼 립시츠 상수란?
Lipschitz function:
\[Let \ a \ function \ f : [a,b] \rightarrow \mathbb{R} \ s.t. \ for \ some\ constant\ \mathbb{M}\ and\ for\ all\ \mathbb{x,y} \in\ [a,b] ,\\ \mid f(x) - f(y) \mid \le M \mid x-y \mid \qquad - (1). \\ Then \ the \ function \ f \ is \ called \ Lipschits\ on \ [a,b], \ and \ one \ writes \ f \ \in Lip([a,b])\](1)에서 x-y로 나누면 결국 미분계수가 M을 넘어가지 않는 함수라고 생각할 수 있다.
- 그럼 Lipschitz 상수는??
→ 미분계수의 최솟값으로 생각할 수 있다!
SN-GAN에서 쓰이는 방법
우리가 GAN을 사용할 때
\[\min_{G}\max_{D}V(G,D)\]인데, 여기서 가정하는 것이 D에 대해 max라는 점 (optimal한 D)
G가 fix되어 있을 때
\[D^{*}_{G}(x) := q_{data}(x) / (q_{data}(x) + p_G(x))\] \[D^{*}_{G}(x) := {q_{data}(x) \over (q_{data}(x) + p_G(x))} \\ = sigmoid(f^*(x) = log_{q_data}(x) - log_{P_G}(x), \qquad (3)\] \[\text{its derivative }, \nabla_x f^*(x)= {1 \over q_{data}(x)} \nabla_x q_{data}(x) - {1 \over P_G(x)}\nabla_x P_G(x) \qquad (4)\]결국 f가 unbounded 되어 있다는 말은 lipschitz 상수 또한 unbounded 되어 있다는 말
→ lipschitz 상수가 bounded 하도록 만들어서 D의 gradient가 폭발하는 것을 막음
\[\underset{\lVert f \rVert_{Lip} \le K}{\arg\max}V(G,D) \qquad (5)\]이렇게 표현이 가능함.
WGAN : weights clipping으로 제약
WGAN-GP : real과 fake에서 sample을 뽑아 gradient를 계산하고, lipschitz constraint를 둠
- 이런 방법들은 local하게 제약이 걸릴 가능성이 높다. → SN
Spectral normalization은 lipschitz constraint가 1이 되도록 Weight matrix를 normalization 하는 것이다.
Hinge Loss
- 두 데이터 분포 간 거리가 가장 먼 decision boundary를 찾기 위해 고안
loss = max{0, 1- (y’ * y)}
y’ : 예측값, y: 실제값
따라서
Dsn : spectral-normalized discriminator, G: image inpainting network
- perceptual loss: 이미 patch-level 정보가 encoded되어서 사용하지 않음
결국 loss는:
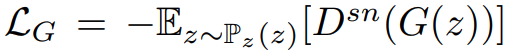
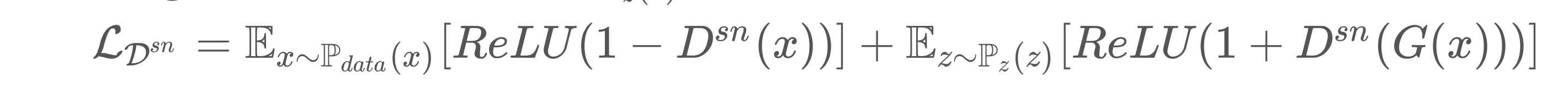
- pixel-wise L1 reconstruction loss
- SN-PatchGAN loss
Architecture
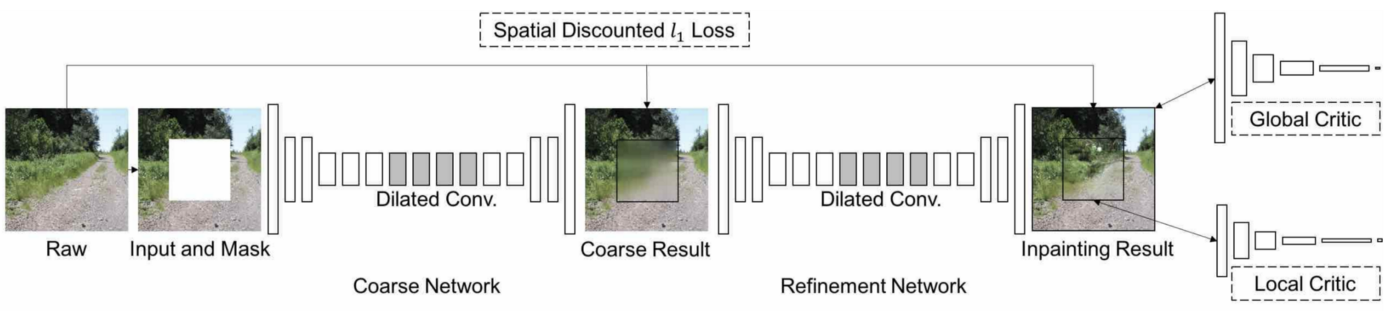
- deepfillv1과 비교해보면, 1) convolution이 gated convolution으로 변경되었고, 2) 2nd generator 부분이 two-branch refinement network with contextual attention으로 변경되었음 3) 하나의 discriminator : local discriminator가 전체 그림을 처리 가능하여 하나로 바뀌었다.
1st generator - for a coarse reconstruction
2nd generator - for a refinement of the coarse filled image
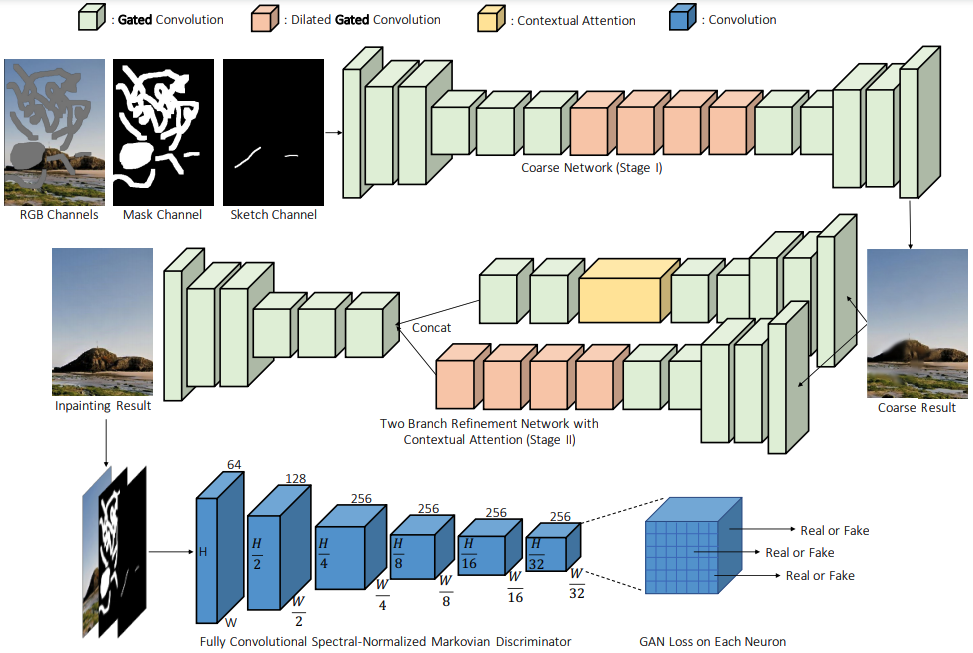
- coarse와 refinement에서는 partial convolution에서 사용되었던 Unet 대신 simple encoder-decoder block이 사용됨 → non-narrow mask에서 UNet의 skip-connection이 큰 영향이 없다고 한다.

(This is mainly because for center of a masked region, the inputs of these skip connections are almost zeros thus cannot propagate detailed color or texture information to the decoder of that region.)
- encoder - decoder 부분에 gated convolution을 적용
- gated convolution의 potential problem : 너무 많은 parameter가 생성됨
→ model의 width를 25%로 얇게 진행되도록 하였다고 함.
Result
Quantitative Result

- learning-based methods perform better than Patch- Match in terms of mean l1 and l2 errors
- partial convolution 결과가 안 좋은 이유: un-learnable rule-based gating
Qualitative Comparisons
-
User-guidance가 없을 때

-
User-guidance가 있을 때
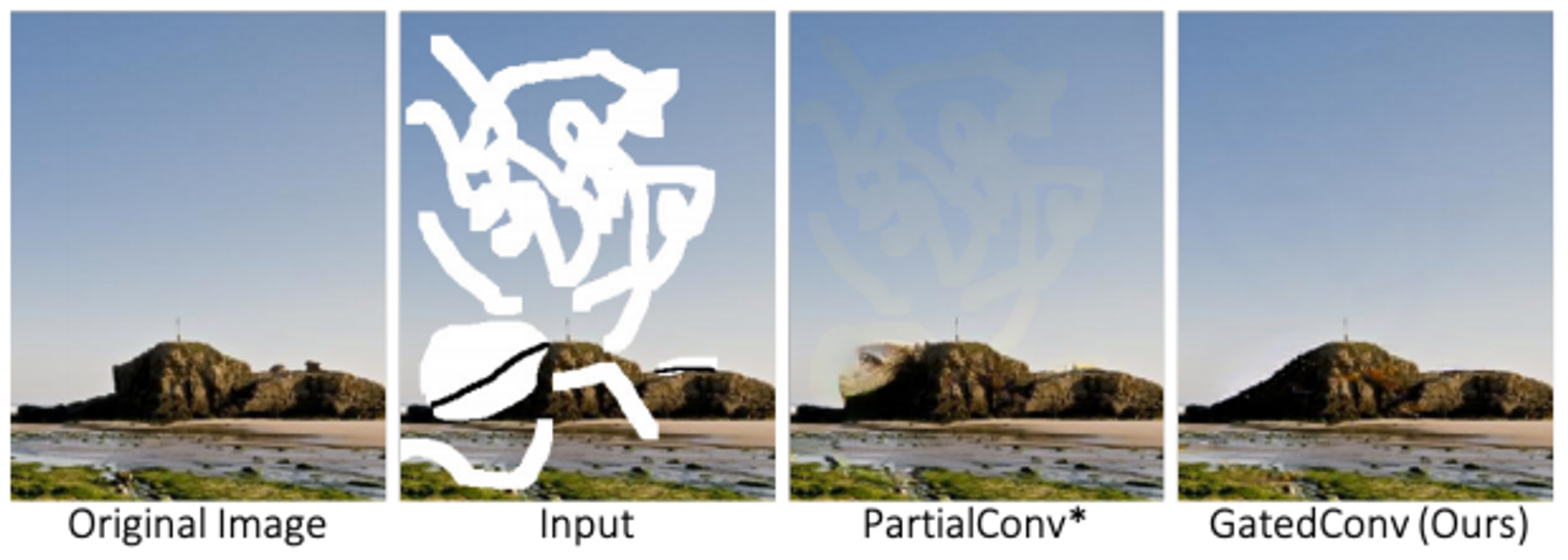 사진을 보면, user-guidance를 처리할 수 있는 건 gated convolution밖에 없음을 알 수 있음.
사진을 보면, user-guidance를 처리할 수 있는 건 gated convolution밖에 없음을 알 수 있음. -
Object Removal and Creative Editing

Photoshop* 2017 - based on PatchMatch
- 따라서 전체 사진에 대해 배우지 않는 traditional한 모델들은 stationary한 사진에서는 잘 작동할 지 몰라도, 사진이 복잡해지면 작동하지 않음
- learning-based by vanilla convolution은 나아졌지만 홀 부근에 artifact를 만듬
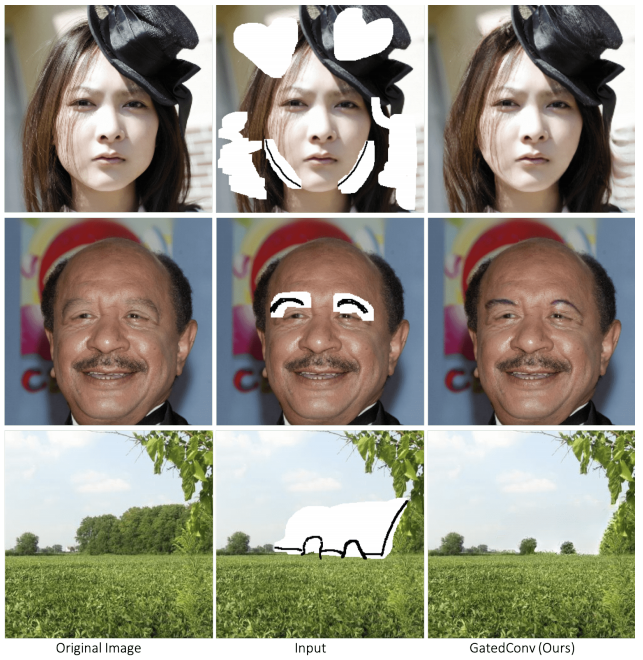

User-guide가 들어가는 사진도 굉장히 잘 처리하는 모습!
4. Discussion
논문의 contribution을 정리해보면,
- convolution 방식의 개선이 이루어졌다 → vanilla convolution, partial convolution, gated convolution
- GAN 성능을 올리기 위한 방법 또한 지속적인 개선이 이루어지고 있다 → WGAN, WGAN-GP, SN-GAN
- User-guide를 처리할 수 있는 방법론의 제안
내가 생각했을 때의 이 논문에서 주목해서 봐야 하는 부분은, 기존의 partialconv에서 0, 1의 binary mask를 사용하는 hard gating 방법론에서, 마스크를 0,1 사이의 값으로 뱉는 soft gating을 사용했다는 점인 것 같다. soft gating을 사용함으로써 user-guide의 처리가 가능해지고, hard gating에서 오던 문제를 해결할 수 있었기 때문이다. 그러나 이 gated convolution이 모델의 parameter를 과도하게 증가시킨 부분이 있으므로, 파라미터를 최적화할 수 있는 방법이 또 있을 수 있을 것 같다.